Introduction to Microsoft Windows Active Directory
Active Directory (AD) is a directory service for Windows domain networks and is generally included as specific processes and services within Windows Server operating systems. It is a database of network resources (i.e. objects) that contains information about each object. Network Neighborhood is a great Windows Server utility for small to medium sized networks.
If you have a large network setup, it may be difficult to find a particular printer or server, especially if you do not know the name of that network item. Furthermore, accommodating such a network, would require partitioning it into several domains connected by trust relationships. AD helps solve many of the problems listed above, offering a new level of scalability and organization to enterprise computing. Each domain directory can store as many as 10 million objects, accommodating millions of users.
AD Structure
The main components that are used to design hierarchy and optimize network traffic are AD’s logical and physical structures. The logical structure utilizes OUs, domains, trees, and forests to organize network resources. It aids in designing a network hierarchy according to organizational needs, as well. As opposed to logical structure, AD’s physical structure consists of sites and domain controllers. A physical structure uses customized network configurations to manage and optimize network traffic.
- Forests Are the highest level AD structure, contain domains and are used to define an administrator’s scope of authority.
- Domains contain OUs and are used to partition directory data, and control replication.
- Organization Units contain users, computers, and accounts, and are used to delegate control and apply policies.
- Domain Trees are compilations of domains that are formed into hierarchical structures. New domains are referred to as children of the tree root domain (i.e. parent).
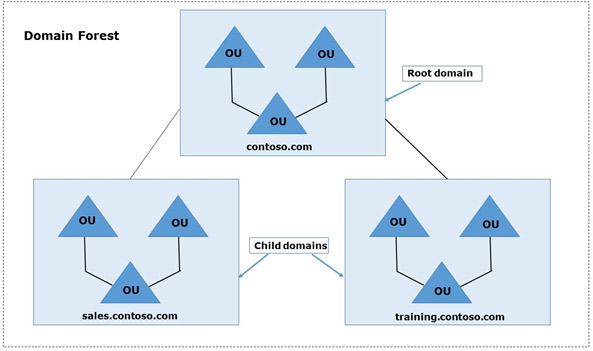
The root domain in the figure above is ‘contoso.com’. There are two child domains in the domain tree with the adjoining namespace ‘contoso.com’: ‘sales.contoso.com’ and ‘training.contoso.com’.
Built-In Active Directory Backup and Restore
We’ll spend the second half of this article guiding you through Active Directory’s backup and recovery options. We’ll begin by showing you two different ways of performing inherent backups. The next article in this series will explore backup and restore options in an AWS hosted environment. As for now, we are using an Amazon EC2 instance with Windows Server 2012 and have installed AD.
Installing and Configuring Backup
The Windows Server 2012 Backup features are not installed by default. In order to install them:
- Log into the system as an administrator, backup operator, or with equivalent privileges
- Execute the following commands from the PowerShell prompt:
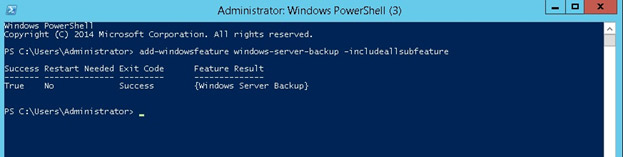
add-windowsfeature windows-server-backup –includeallsubfeature [enter]
By running the command above on PowerShell, you will see the screen below when the backup features have installed successfully.
Once you have installed the Windows backup feature, you will be able to back up the domain controller using various methods, which we will outline a bit later in this article.
System State Backup
System state backup data consists of all system data, such as boot files, system files, AD, SYSVOL, cluster DB, registry and more. Whenever a system state backup or restore is performed, it cannot be broken up into individual components due to its dependencies on the system state components. Though system state backups can be performed in any order, recovering the system state will first replace boot files and commit the system hive of the registry as a final step in the process.
In order to schedule a system state backup:
- Log into the system as an administrator, backup operator, or with equivalent privileges
- Execute the following command from an elevated command prompt:
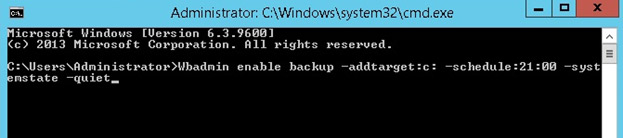
Wbadmin enable backup -addtarget:<target> -schedule:21:00 –systemstate –quiet
As seen in the image below, set Windows C or D drive as the target location to perform Active Directory backup.
We can also manually perform Active Directory system state backups using wbadmin.
In order to create a manual system state backup:
- Log into the system as an administrator, backup operator, or with equivalent privileges
- Execute the following command from an elevated command prompt:
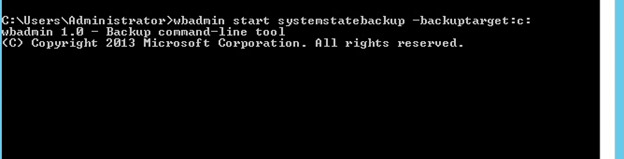
Wbadmin start systemstatebackup –backuptarget :<drive> -quiet
As you can see below, we have used the C drive as a backup target for manual backup, however you can define your own path for a backup target.
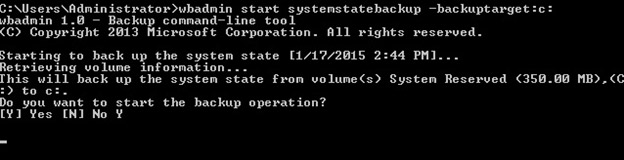
Once you press Enter, it will ask if you want to start the backup operation. As shown below, press ‘Y’ to continue:
Having demonstrated how to perform a system state backup as an administrator or backup operator, we’ll now explore another type of domain controller backup—snapshot backups.
Snapshot Backup
Microsoft began supporting a feature with Windows Server 2008, that allows administrators to create snapshots of Active Directory databases. This mechanism is known as Snapshot Backup. An advantage of this feature is that it allows offline use, enables administrators to mount a backup of an AD structure under a different set of ports to provide read-only access of backups through LDAP. This is very helpful if property is accidentally changed and an administrator wants to find those changes. This can be done by setting up a read only backup on another port to find the modified data.
Active Directory uses NTDSUtil to create snapshots. This can be used to create a single, one-time snapshot or scheduled snapshot backups.
In order to manually create and view AD snapshots:
- Log into the system as an administrator, backup operator, or with equivalent privileges
- Run NTDSUtil from the elevated command prompt
- Activate the current NTDS instance by entering: Activate Instance NTDS
- Change the snapshot component of NTDSUtil by entering: snapshot
- Create a snapshot by entering: create
- View all current snapshots (NTDSUtil and system state backup) by entering: list all.
You can automate NTDSUtil by writing all commands in a single command line, then scheduling that line using Windows OS’ built-in scheduling service.
In order to launch a snapshot from a single command line:
- Log into the system as an administrator, backup operator, or with equivalent privileges
- Execute the following command from an elevated command prompt:
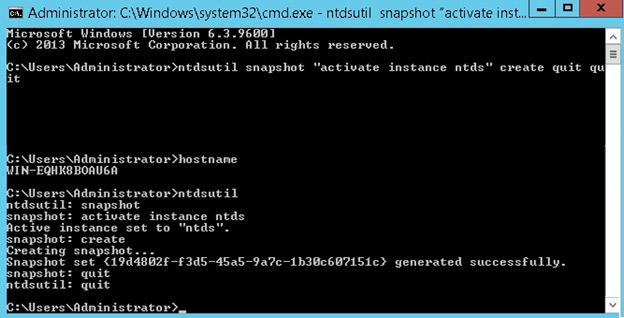
ntdsutil snapshot “activate instance ntds” create quit quit
The screenshot above demonstrates how you can create a snapshot from a single command.
Restoring Active Directory
Backup administrators are faced with the crucial task of restoring a server to its normal state. In this section, we will go through how to restore Active Directory to its normal state.
1. Authoritative Restore of Active Directory
Authoritative restore is the method of restoring a system state backup. If you accidentally delete an OU, group, or a user account, an authoritative restore needs to be performed for the deleted Active Directory object.
- To do this you will need to boot into DSRM (Directory Services Restore Mode) by restarting your server and pressing F8 during the restart.
- Choose Directory Services Restore Mode from the Advanced Boot menu.
- Log into your server with the DSRM password you created during AD installation.
- Once you’re logged into your server in DSRM safe mode, open a command prompt by clicking Start, type “cmd“, and press Enter.
- To make sure you restore the correct backup it’s a good idea to use the “wbadmin get versions” command and write down the version you need to use.
- To perform a nonauthoritative restore of Active Directory, enter: “wbadmin start systemstaterecovery -version:01/18/2015-02:39“.
Note: The backup version will vary depending on your situation. Type “y” and press Enter to start the non-authoritative restore. - Go grab some coffee and take a break while the restore completes.
- You can mark the SYSVOL as authoritative by adding the –authsysvol switch to the end of the wbadmin command.
2. Snapshot Restore of Active Directory
The snapshot feature has been available since Windows Server 2008, and makes restoring AD snapshots very easy.
In order to restore your snapshots, follow the steps below:
- Log into the system as an administrator, backup operator, or with equivalent privileges
- Run NTDSUtil from the command prompt
- Change the snapshot component of NTDSUtil by entering: snapshot
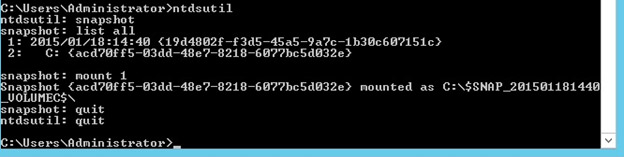
- List all of the snapshots that were taken by entering: list all
- Identify the snapshot number you’d like to restore by entering: mount 1
And there you have it. In this article, we have demonstrated how to simply back up and recover Active Directory. In part two of this series, we will show how to perform backup and recovery when AD is configured in AWS.
Try N2WS Backup & Recovery (CPM) for FREE!
Read Also