One of the most popular AWS services is the managed relational database offering known as Amazon Relational Database Service (AWS RDS). AWS RDS offers an on-demand available, scalable, cost efficient and easy to manage RDBMS in the cloud. RDS uses EBS volumes internally for persistent storage and there are different AWS RDS instance types.
Unlike EBS backed EC2 instances, RDS does not have a stopped state, so it will keep running until it is terminated by a user. Although RDS instance type modifications cause database downtime, if your application implementation permits, it can be a good option to optimize costs.
Aside from using N2WS to schedule instances to shut down during off-peak hours, another way to save on costs with RDS, is to change the size of your RDS instances.
In this article, we’ll show you how to modify the size of an RDS instance manually using the AWS console. More specifically, we will modify the AWS RDS instance type from medium to micro using the AWS console as well as the AWS CLI.
Modifying AWS RDS instance types
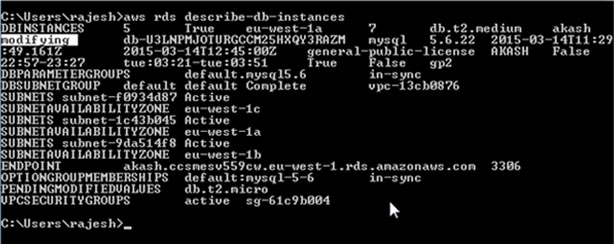
In the following example, we’ll use a MySQL AWS RDS instance with a db.t2.medium RDS instance class.
aws rds describe-db-instances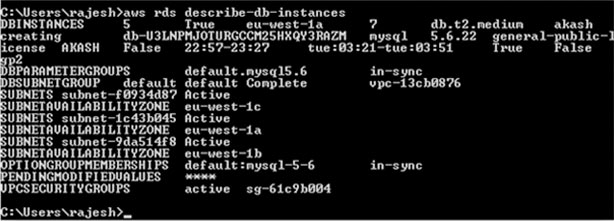
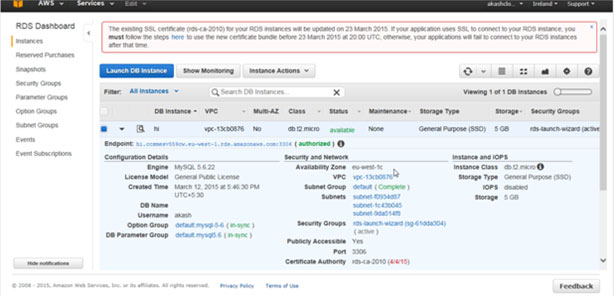
You can change the RDS instance class from db.t2.medium to db.t2.micro by clicking on ‘Modify DB Instance’ under the ‘Actions’ tab, as shown below:
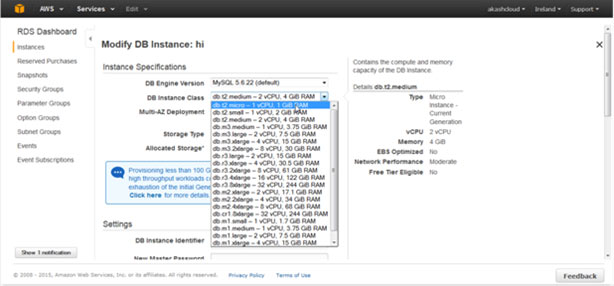
aws rds modify-db-instance --db-instance-identifier akash --db-instance-class db.t2.micro --apply-immediately 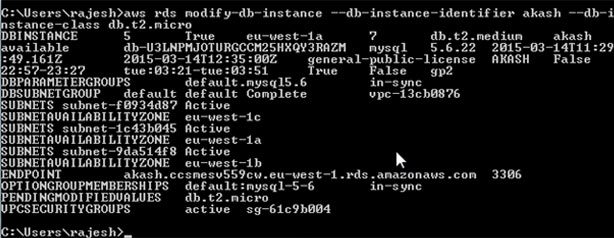
Select ‘Apply Immediately’ to instantly modify your DB instance, otherwise the modification will be performed in the following maintenance window.
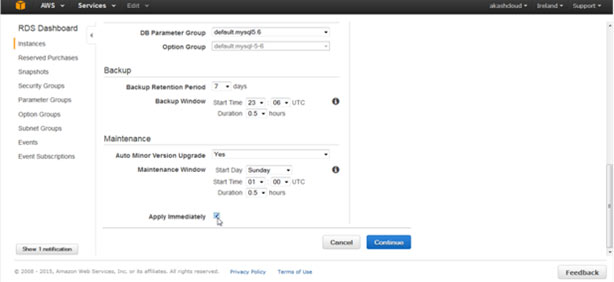
This shows you that your AWS RDS instance is being modified:
Once complete, your DB will be up and running with the modified db.micro instance.
aws rds describe-db-instances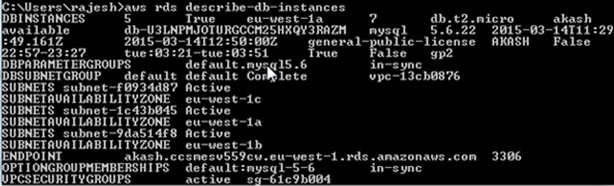
- Plan instance modifications during maintenance windows: To avoid unplanned downtime, schedule RDS instance modifications during pre-configured maintenance windows if "Apply Immediately" is not critical. This ensures minimal disruption to production workloads.
- Evaluate workload requirements before switching instance types: Always assess the CPU, memory, and I/O demands of your application before changing instance types. Scaling down without understanding your resource needs can lead to performance bottlenecks.
- Enable Multi-AZ for seamless failover: If running critical workloads, enable Multi-AZ deployments before modifying instance types. This minimizes downtime during instance modification as failover can happen to the standby instance.
- Use automated snapshots for extra backup coverage: Although AWS provides automated backups, configure manual snapshots before modifying the instance type to safeguard against unforeseen failures during the change process.
- Optimize storage alongside instance resizing: Evaluate your storage type and size when modifying instance types. Pair instance resizing with a switch to Provisioned IOPS or General Purpose SSD if needed, ensuring optimal storage performance.
Backup Your RDS
It is also very important to backup your DB instance before performing any size changes to the AWS RDS instance. The database instance may fail to start as the result of an error, in which case you can recover the data with your backup. AWS RDS offers two kinds of backup solutions. One is with EBS snapshots, which is a point-in-time backup and allows you to recover data from the exact point in time when that snapshot was created.
The other option is with automated backups, where daily backups are performed at a predefined time so data can be recovered along with its transaction log, RDS ensures data recovery from any point in time to provide better backup solutions. N2WS Backup & Recovery is an enterprise-class backup and disaster recovery solution for EBS volumes and RDS databases. It is available as a service, allowing you to register multiple AWS accounts. You can configure policies and schedules to take automated snapshot backups of RDS. Additionally, you can configure policies to remove old snapshots.
N2WS provides automated and regular backups of AWS RDS instances:
- Flexible backup policies and schedules
- Consistent database backup for SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, MongoDB, etc
- Instance and data recovery across AWS regions in seconds
- “Pull” and “Push” based alerts and notifications
- Application consistent backup
- Automated backup based on Tags
- Resource Control, to turn off RDS instances on a schedule or on demand
Fortify your cloud across every critical dimension.
- Efficiency + Optimization
- Security + Control
- Orchestration + Visibility
