What Are Cloud Backup Services?
Cloud backup services store and protect data by copying files from local machines or servers to remote cloud storage. This ensures data safety against physical loss or corruption due to hardware failures or disasters. These services typically automate the backup process, so users don’t have to manually save files to the cloud regularly.
Storing backups in the cloud offers accessibility from any location with an internet connection. This allows organizations and individuals to restore data quickly without physical media. Additionally, many cloud backup services offer features such as encryption and versioning, improving data management security.
There are many cloud backup services available, some of them suitable for individuals or small businesses, and some for larger organizations. In this article we’ll focus on enterprise cloud backup services intended for larger organizations or those with complex backup or compliance requirements.
This is part of an extensive series of guides about data breaches.
In this article:
- Key Features of Enterprise Cloud Backup Services
- Implementing Cloud Backup Strategies with Backup Services
- Notable Cloud Backup Services
Key Features of Enterprise Cloud Backup Services
Cloud backup services intended for organizations typically offer the following capabilities.
Automatic Backups
Automatic backups simplify data protection by eliminating the need for manual operation. These systems continuously monitor files and automatically upload changes to the cloud at scheduled intervals. This ensures data is consistently protected without user intervention, preventing human error.
Such services often offer customization options, allowing users to define backup frequency and select specific files or folders for automatic updating. This ensures that only critical files are backed up, optimizing storage usage and reducing unnecessary data transfer.
Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery ensures continuity in business operations after a data loss event, such as natural disasters or cyber-attacks. Cloud backup services promise swift data restoration, minimizing downtime and preserving business integrity.
Utilizing versions stored in the cloud, organizations can quickly recover and resume operations with minimal disruption. Cloud-based disaster recovery is typically more cost-effective compared to traditional methods, which rely on physical hardware and offsite storage.
Versioning
Versioning keeps multiple iterations of files, enabling users to revert to previous versions when necessary. This is useful when files are mistakenly altered or deleted, allowing quick restoration to a desired state. By maintaining a history of changes, cloud services enhance data accuracy and usability.
Most cloud backup services allow users to set retention policies for versions, determining how long versions are retained before deletion. This provides users with control over storage space management while ensuring essential versions are readily available when needed.
Data Compression and Deduplication
Data compression and deduplication optimize storage and transfer data efficiently. Compression reduces the size of files before uploading them to the cloud, saving bandwidth and storage space, which can significantly lower costs.
Deduplication eliminates redundant copies of data, ensuring efficient storage utilization. These technologies streamline the backup process, making it more feasible for large data volumes.
Data Encryption
Data encryption encodes data before transmission to the cloud, making it inaccessible to unauthorized users. This ensures data privacy, protecting sensitive information from breaches or cyber threats.
Cloud backup providers usually offer end-to-end encryption, ensuring data remains encrypted from local storage to cloud servers and back again. This protection guarantees that only authorized users with decryption keys can access the data.
Cross-Platform Support
Cross-platform support is the capability of cloud backup services to work across multiple operating systems and devices. Such services maintain consistent functionality, whether users are on Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, or Android, ensuring broad accessibility and usability.
By supporting various platforms, cloud services enable integration within different infrastructures, simplifying backup and recovery processes. Organizations benefit from a unified approach to data protection, minimizing compatibility issues.
Implementing Cloud Backup Strategies with Backup Services
Here are several backup strategies typically supported by cloud backup services:
3-2-1 Backup
The 3-2-1 backup strategy is a widely recommended approach for data protection that involves maintaining three total copies of data: the original file plus two backups. One backup is kept on local storage for quick access, while the second is stored offsite, typically in the cloud, to protect against physical disasters affecting local data.
By following this strategy, organizations achieve a balance between accessibility and security. The cloud component ensures a secure offsite copy, protecting against events like hardware failures or theft, while the local backup provides immediate access for recovery if needed. Many cloud backup services support this model by offering integrations with local storage solutions.
Incremental Backups
Incremental backups focus on backing up only the changes made since the last backup, whether that backup was full or incremental. This process is highly efficient, reducing the amount of data transferred and stored with each backup, which saves bandwidth and storage space.
Most cloud backup services support incremental backups by tracking changes in files, allowing rapid and resource-effective backups. These backups also speed up the recovery process by minimizing the amount of data that needs to be downloaded for a restore. Incremental backups are useful for frequently changing data.
Differential Backups
Differential backups save all changes made since the last full backup, making it faster to restore data than incremental backups, which require multiple sessions to reconstruct data. With differential backups, only two backup files are needed to recover the latest version of the data: the last full backup and the most recent differential backup.
Cloud backup services supporting differential backups provide a middle-ground option between incremental and full backups, optimizing recovery time. This strategy is suitable for organizations needing to balance data retrieval speed with cost savings, as fewer files are required for recovery while still reducing storage compared to daily full backups.
Mirror Backups
Mirror backups create exact, real-time replicas of files and folders in their current state, updating them in the cloud as changes occur. This approach ensures that the backup is always synchronized with the latest data, providing immediate access to current files in case of a system failure.
While mirror backups don’t retain historical versions of files, making them less effective for restoring previous file states, they’re useful for maintaining a continuously updated dataset. Many cloud services offer mirror backup as an option for data that requires real-time synchronization, such as project files or databases.
- Integrate granular access controls: Use role-based access and identity management to ensure only authorized users access specific backup functions or data. This can limit exposure in case of a breach.
- Use hybrid backup strategies: Complement cloud backups with on-premises backups for critical files. Hybrid strategies provide faster restoration times for frequently used data while ensuring long-term offsite protection against disasters.
- Leverage immutable storage for ransomware protection: Use immutable storage features offered by advanced backup solutions, which prevent data deletion or modification once written, safeguarding backups against ransomware attacks on backups.
- Implement multi-cloud storage redundancy: For critical data, consider using multiple cloud providers to diversify risk. Multi-cloud redundancy can protect against provider-specific outages and offer more geographic redundancy for disaster recovery.
- Compress and archive older data to cold storage: For older, less critical data, use cold storage or infrequently accessed storage options to reduce costs. This also reduces the bandwidth impact of regular backups.
Notable Cloud Backup Services
1. N2W
N2W is a purpose-built solution designed to deliver enterprise-grade backup, disaster recovery, and data lifecycle management for both AWS and Azure workloads. Its seamless integration with cloud services, coupled with features like cost optimization and instant recovery, makes it a preferred choice for organizations operating in single-cloud or multi-cloud environments.
Key Features of N2W:
- Instant Recovery: Enables one-click recovery of cloud workloads, including entire instances, volumes, and files, significantly reducing downtime during outages or cyberattacks.
- Cross-region and cross-account disaster recovery: Automates backups and replication across regions and accounts in both AWS and Azure, ensuring high availability and robust protection against account or region-specific failures.
- Cost optimization tools: Provides advanced scheduling and tiering options to automatically move snapshots to cost-efficient storage solutions like Amazon S3 Glacier, Azure Blob Storage, or Wasabi.
- Granular file-level recovery: Allows users to browse and restore individual files or directories from any backup without requiring pre-indexing or separate tools.
- Application-consistent backups: Ensures databases and applications, such as Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, and SAP HANA, are captured in a consistent state for reliable restoration.
- Backup auditing and reporting: Delivers real-time insights into backup health, compliance, and storage usage with customizable reports and dashboards.
- Seamless integration with AWS and Azure services: Natively integrates with services like Amazon EC2, Amazon RDS, Azure VMs, and Azure SQL Database for comprehensive data protection.
- User-friendly interface: All tasks, from setup to complex recovery scenarios, can be performed within the UI, eliminating the need for scripting while offering API options for those who prefer automation.
Limitations of N2W Backup & Recovery:
- No native SaaS application backup: While N2W excels in cloud infrastructure protection, it does not natively support SaaS platforms like Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace, requiring additional tools for those workloads.
- Focused on cloud environments: N2W does not directly support on-premises workloads, which may be a consideration for organizations with hybrid setups.
- Additional storage costs from providers: While N2W itself does not charge extra for retention, organizations should account for any incremental costs from their cloud storage provider (e.g., for using Amazon S3 Glacier or Azure Archive Storage for long-term retention).
Overall it’s a robust solution for businesses leveraging AWS, Azure, or both. It simplifies cloud-native backup and disaster recovery with unmatched flexibility, cost-saving capabilities, and a user-friendly interface. For enterprises looking to secure their critical workloads with minimal effort, N2W stands out as a trusted partner.
2. AWS Backup
AWS Backup is a service that centralizes and automates snapshot creation across AWS services and hybrid workloads. It enables organizations to define backup policies, known as backup plans, which specify backup frequency and retention periods. By assigning resources to these plans, AWS Backup automates the creation and management of backups.
Key features of AWS Backup:
- Centralized backup management: Provides a unified console to manage backups across various AWS services, including Amazon EBS, Amazon RDS, and Amazon S3—as long as they are in the same AWS account.
- Policy-based automation: Users can create backup plans that define parameters such as backup frequency and retention periods.
- Cross-region backup: Supports copying backups across different AWS Regions, improving disaster recovery capabilities.
- Data encryption: Backups are encrypted both in transit and at rest using AWS Key Management Service (KMS) keys, ensuring that data remains secure throughout the backup and restore processes. However, backups encrypted without default keys cannot be copied across regions.
- Backup vaults and access control: Stores backups in backup vaults, which are logical containers that help organize and secure backups. Access to these vaults can be controlled using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies.
- Compliance and auditing: Integrates with AWS Backup Audit Manager, allowing organizations to monitor and report on the compliance of their backup activities. This integration provides insights into backup operations and helps ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
Limitations of AWS Backup:
- No one-click restore: Requires automation of restore operations via API calls, which suits DevOps-savvy businesses but may lack ease for users needing simple recovery. N2W, by contrast, offers near-instant one-click recovery without scripting.
- No granular recovery: Only supports full-server recovery, lacking file/folder-level granularity. N2W fills this gap by enabling detailed searches and drill-down access across multiple backup generations, eliminating the need for pre-planned indexing.
- Uses expensive storage tiers: AWS Backup defaults to costly storage tiers like Standard S3, which can dramatically drive up the cost of backup storage.
- No disaster recovery support: Allows manual snapshot copying to another region but doesn’t automate recovery. Cross-account disaster recovery, critical for safeguarding against account compromises, is absent but essential for robust multi-account AWS setups.
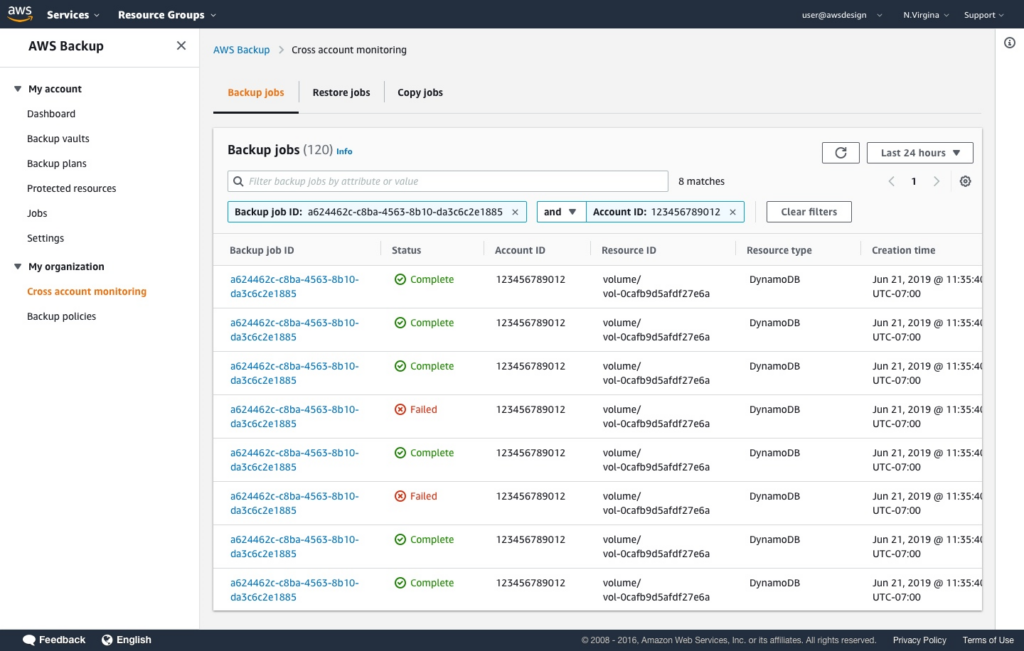
Source: Amazon
3. Carbonite
Carbonite Cloud-to-Cloud Backup, powered by OpenText, is a secure and automated solution to protect data stored in popular SaaS applications such as Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Salesforce, Box, and Dropbox.
Key features of Carbonite:
- Automated daily backups: Automatically backs up data from Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Salesforce, Box, and Dropbox on a daily basis.
- Granular data recovery: Recovers data from any point in time with granular restore options, including by date, attachment, or keyword.
- Global data centers: Data is securely stored in Carbonite’s data centers located across the globe, including regions such as the U.S., Canada, Europe, and Asia.
- Ransomware and malware protection: Protects data from ransomware, malware, and data breaches.
- Compliance ready: Ensures backups are encrypted and compliant with industry standards such as CCPA, FINRA, HIPAA, and GDPR.
Limitations of Carbonite:
- Limited speed control: While Carbonite allows users to throttle internet usage, the feature lacks granular control, which may frustrate those trying to optimize bandwidth usage.
- Poor backup speeds: Users frequently report slow upload and download speeds, which can hinder efficiency, especially for large files or extensive datasets.
- Limited feature set: Personal plans do not support hybrid backups, NAS uploads, or block-level algorithms, restricting functionality for non-enterprise users.
- No mobile app support: Carbonite does not offer mobile apps for Android or iOS, limiting cloud backup capabilities for mobile device users.
- No linux compatibility: The service is not available for Linux systems, narrowing its usability for diverse IT environments.
- No image-based backups for personal plans: Creating a full system image backup is restricted to server plans, limiting the use of personal and non-enterprise plans.
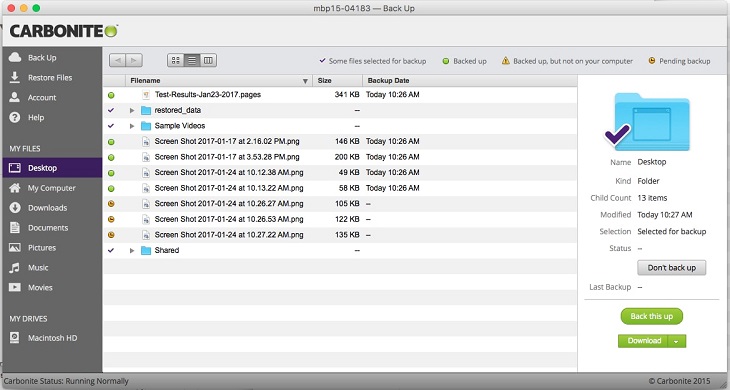
Source: Carbonite
4. Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud
Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud is a solution combining backup with other cybersecurity capabilities to protect client workloads across more than 20 platforms. Tailored for managed service providers (MSPs), this platform provides backup, AI-based anti-malware, and endpoint protection in an integrated system.
Key features of Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud:
- Backup and recovery: Offers full-image and file-level backup, enabling rapid recovery of data and workloads with near-zero Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs).
- AI-based malware and ransomware protection: Uses AI-driven detection to block malware, ransomware, and zero-day attacks.
- Centralized management for MSPs: Provides integration with remote monitoring and management (RMM) and professional services automation (PSA) systems, allowing MSPs to manage backup, security, and endpoint protection from a single dashboard.
- Security features: Includes options to add protection packs like Extended Detection and Response (XDR), Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), Disaster Recovery, and Data Loss Prevention (DLP).
- Disaster recovery: Offers a disaster recovery option that ensures rapid business continuity by restoring critical systems and data after incidents like hardware failures or cyberattacks.
Limitations of Acronis:
- Limited customer support on weekends: Users have reported dissatisfaction with the lack of support during weekends, a critical period for many organizations performing disaster recovery (DR) tests or backups.
- Complex access control: The technical documentation for configuring access control is not well-explained, leading to challenges in implementation and administration.
- Inconsistent onboarding: Some users experienced issues during onboarding due to changes in account representatives and unclear credit and setup processes.
- Overwhelming product range: While Acronis offers a broad suite of features, the learning curve can be steep. The partner portal includes resources, but best practices can be challenging to interpret without additional guidance.
- Non-intuitive interface: Setting up backups, especially selecting files and folders, can be cumbersome. Users must rely on third-party tools like TreeSize to estimate folder sizes, which adds to setup time.
- Inefficient backup connection process: When connecting an old backup to a new PC, the process can be lengthy and error-prone, potentially resulting in wasted storage space.
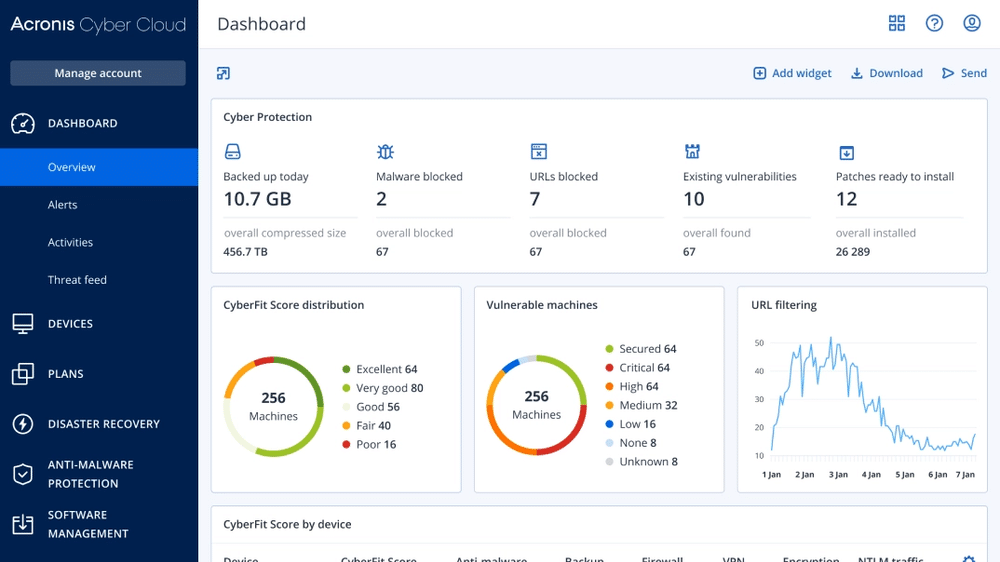
Source: Acronis
5. Veeam Backup
Veeam Backup & Replication offers a solution for securing backups, ensuring clean recovery, and building data resilience across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. With a focus on ransomware protection, rapid recovery, and seamless management, Veeam helps organizations maintain control over their data and recover from cyberattacks or system failures.
Key features of Veeam Backup & Replication:
- AI-powered threat detection: Uses AI-based malware detection to monitor backups and flag threats during the process.
- Hybrid cloud backup: Protects critical workloads in hybrid and multi-cloud environments with secure backup solutions for AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Immutable backups and zero trust architecture: Locks down backups with immutable storage and advanced security controls, including zero trust principles and “four eyes” admin protection.
Cons of Veeam Backup:
- Limited deployment options: Deployment of Veeam Backup for AWS is restricted to CloudFormation templates, offering less flexibility compared to solutions that support manual deployment or custom naming conventions.
- Complex backup configuration: Setting up backup policies is not user-friendly and often requires tagging resources, making it difficult to exclude specific volumes without in-depth knowledge of the infrastructure.
- Lack of multi-tenancy: The solution does not support multi-tenancy, limiting its use for MSPs who need to provide separate backup consoles for individual clients.
- Outdated terminology: Veeam uses on-premise terminology for cloud solutions, such as referring to backups as “replicas,” which can confuse users accustomed to modern cloud terminology.
- Recovery limitations: The recovery process is cumbersome, requiring users to know specific resources for restoration, as policies are not searchable or linked to the recovery workflow.
- File-level recovery concerns: File and folder-level recovery allows restoring to the same instance, raising potential security risks as this access could inadvertently introduce malware.
- Immutability gaps: Veeam does not support immutable EBS snapshots for AWS but does offer S3 object lock for certain storage classes. However, it lacks support for cost-efficient options like S3 Infrequent Access.
- Ineffective cost estimation: The cost estimation tool for archives often provides inaccurate calculations due to its inability to account for all variables, reducing its utility for budget planning.
- Inefficient cleanup: Unused backups can only be cleaned up once daily, potentially leading to unnecessary storage costs until the next cleanup cycle.
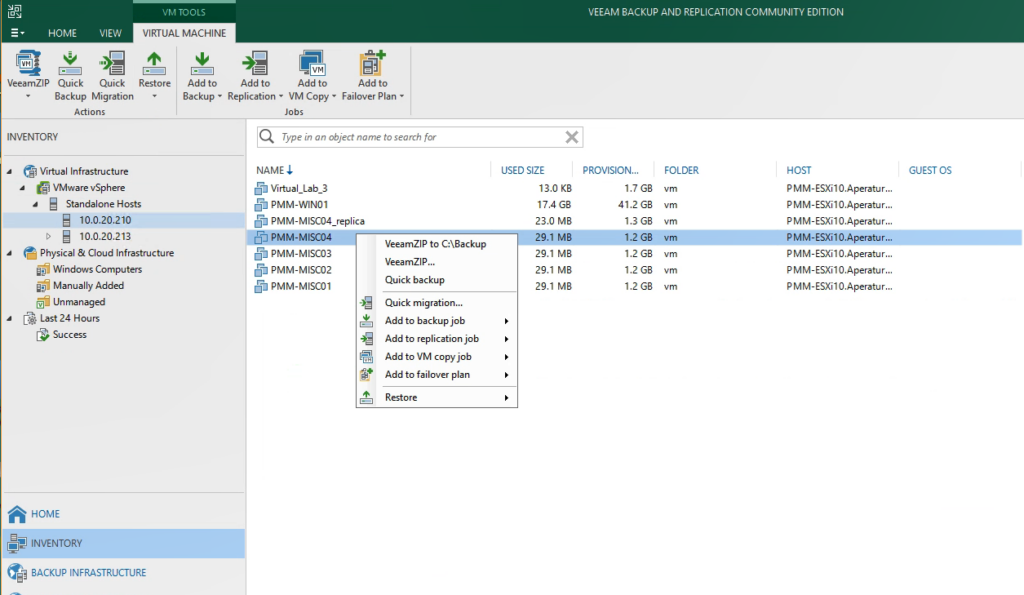
Source: Veeam
Related content: Read our guide to Replication vs Backup
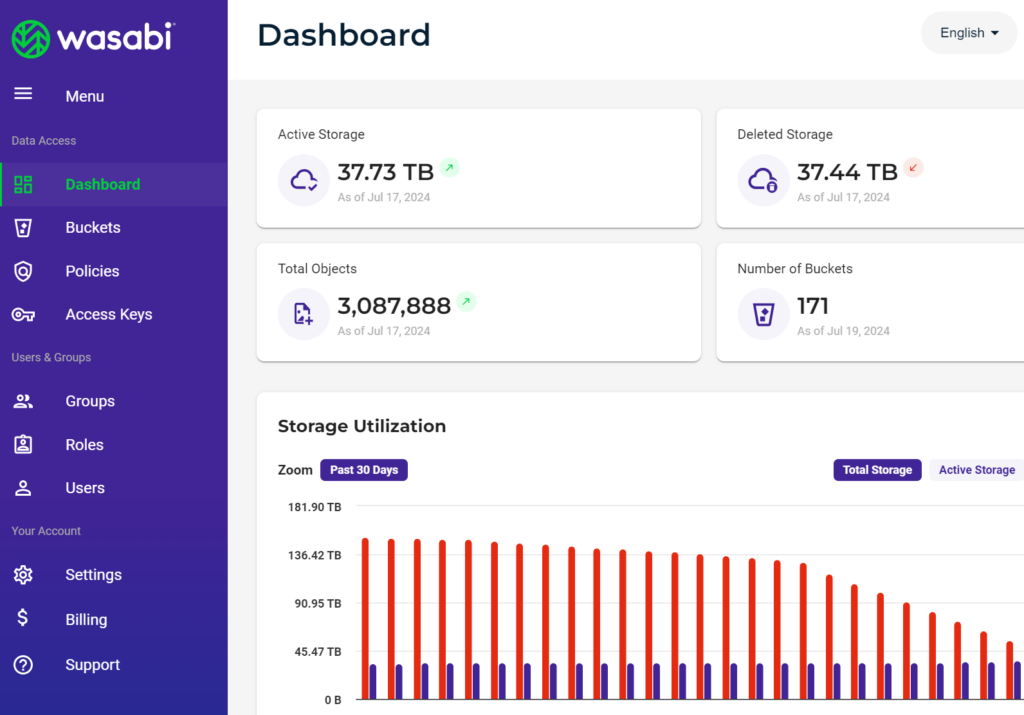
6. Wasabi
Wasabi is a predictable cloud storage service that eliminates egress fees, API charges, and other hidden costs. It offers a single-tier “hot” cloud storage solution that is priced close to cold storage but delivers high-speed data access.
Key features of AWS Backup:
- Pricing: Offers cloud storage priced up to 80% less than some major providers, with no fees for data egress or API requests. ✅ TIP: You can archive AWS or Azure snapshots into Wasabi storage with N2W to save money on long-term backup retention.
- Universal hot storage: Provides a single-tier, high-speed storage solution, suitable for backups.
- Ransomware protection: Implements object-level and bucket-level immutability, safeguarding data from tampering, encryption, or deletion.
- Global data centers: Operates in 15 secure and redundant regions worldwide, maintaining consistent low rates across all locations.
- Security: Features encryption for data in transit and at rest, along with multi-factor authentication (MFA), single sign-on (SSO), and unique account security measures.
- Data migration support: Offers tools for fast migration from on-prem or hyperscale clouds, including coverage of egress fees.
Cons of Wasabi:
- Confusing billing model: Users report difficulty understanding Wasabi’s billing practices, including unexpected charges for deleted or unused data due to minimum retention periods.
- Retention policy charges: Deleted objects are billed for a minimum of 30 days, even if removed immediately, causing dissatisfaction among customers who expect real-time cost adjustments.
- User interface limitations: The console and tools for managing access controls and bucket permissions are described as overly technical, requiring documentation or examples to configure effectively.
- Unreliable object availability: Some users report object availability rates as low as 99.9%, with occasional outages or delays in accessing stored objects.
- Support responsiveness: Despite offering premium support plans, responses during critical outages or billing issues have been noted as slow and inadequate.
- Enterprise suitability issues: Wasabi’s features and support are perceived as insufficient for large-scale enterprise needs, with concerns about data loss during outages.
Source: Wasabi
7. Druva
Druva is a SaaS-based data security platform to protect and recover data from threats. This cloud-native platform provides data protection, accelerated recovery from cyber incidents, and enhanced compliance management.
Key features of Druva:
- SaaS-first data protection: Modernizes backup, disaster recovery, and archiving with a fully cloud-native platform.
- Coverage: Protects data across a range of environments, including public cloud (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud), hybrid setups, endpoints (Windows, macOS, Linux), and SaaS applications like Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and Salesforce.
- Cyber response and recovery: Offers security features like threat hunting, 24/7 monitoring, proactive notifications, and managed detection and response (MDR).
- eDiscovery and compliance: Simplifies data governance with built-in tools for eDiscovery, legal holds, and sensitive data governance. Druva meets key compliance standards including SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, and FedRAMP.
Limitations of Druva:
- Dependency on SaaS infrastructure: As a fully SaaS-based solution, Druva relies entirely on its cloud-hosted interface. If this interface experiences downtime, users are unable to manage or recover backups until the issue is resolved, with no control over resolution timelines.
- Limited AWS region support: Druva supports only 14 AWS regions and GovCloud, restricting flexibility compared to cloud backup solutions with broader global region support.
- Rigid scheduling options: Backup policies in Druva are limited to daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly schedules, lacking the granularity offered by competitors that support minute-level scheduling.
- No cross-cloud support: Druva does not provide functionality for cross-cloud backup or recovery, limiting versatility for multi-cloud strategies.
- Learning curve: Some users find Druva less intuitive compared to alternatives, which offer simpler and more user-friendly interfaces.
Source: Druva
8. Commvault
Commvault offers a cloud backup and data recovery solution to protect data across all environments—on-premise, in the cloud, and in SaaS applications. Leveraging Metallic AI, it provides organizations with cyber resilience through a single platform.
Key features of Commvault:
- Unified data protection: Provides backup and recovery across all environments, including SaaS applications, cloud-native workloads, and on-premise data centers, managed from a single interface.
- Cleanroom recovery: Ensures safe and clean recovery by isolating clean data in a secure environment, protecting against malware reinfection and ensuring recovery integrity.
- Auto recovery: Automates data protection and near real-time recovery processes, leveraging multi-layered security to defend against cyber threats and restore data quickly.
- Risk analysis and compliance: Identifies and classifies sensitive data, ensuring compliance with industry regulations and standards.
Limitations of Commvault:
- Access management concerns: As a SaaS solution, Commvault’s reliance on cloud-hosted services raises potential privacy and access management challenges for organizations handling sensitive data.
- Limited snapshot archiving: Commvault cannot archive RDS snapshots to cold storage solutions like S3 or Azure Blob, which limits cost-effective long-term storage options.
- Complex cross-cloud recovery setup: While cross-cloud recovery is supported, it requires a virtual server acting as an HTTP/HTTPS proxy, introducing additional costs and a potential single point of failure.
- Restricted DR backup flexibility: Disaster recovery backups must be stored in object storage (e.g., S3 or Azure Blob), which can lead to longer recovery times compared to snapshot-based DR backups.
- Challenging infrastructure optimization: Architecting and scaling deduplication servers and optimizing backup jobs require expertise, making the platform less accessible for teams without dedicated specialists.
- Policy limitations: Users cannot include multiple resource types in a single backup policy, which may complicate backup management for diverse workloads.
- Incomplete VPC backup support: Commvault only backs up attributes of EC2 instances within a VPC, not the entire VPC itself, limiting comprehensive recovery options for cloud environments.
- No VPC cloning or recovery scenario features: The platform lacks tools to easily clone VPCs or orchestrate rapid, full-infrastructure recovery, reducing efficiency during large-scale disaster recovery operations.
Source: Commvault
9. Backblaze
Backblaze is a cloud storage service offering always-hot object storage that’s compatible with various platforms and infrastructures. It emphasizes affordability and data management. Its integration capabilities and flexible API support easy deployment.
Key features of Backblaze:
- S3-compatible cloud storage: Provides always-hot object storage compatible with S3, allowing integration with existing systems and tools at a fraction of the cost.
- Enterprise-grade security: Offers encryption, server-side encryption (SSE), and access management features to ensure data protection. Object Locks ensure data immutability, preventing unauthorized changes or deletions.
- Cost-effective pricing: At 1/5th the cost of AWS S3, with three times the free egress.
- Cloud replication: Allows users to set up replication rules to automatically copy and store data in multiple locations, supporting redundancy and faster local access.
- Object lock for ransomware protection: Implements WORM (write once, read many) policies to protect data from ransomware by preventing unauthorized modifications or deletions.
Limitations of Backblaze:
- Unintuitive user interface: Users report challenges with the front-end user experience, particularly frequent logouts during administrative tasks. This disrupts workflow, especially when switching between tasks or managing buckets.
- File retrieval challenges: Retrieving files from backups can be cumbersome, indicating a need for improvement in the accessibility or intuitiveness of the retrieval process.
- Complex reporting: Regular reports provided by Backblaze are not always user-friendly for non-technical users, making it difficult for laypersons to interpret key information.
Source: Backblaze
Conclusion
Cloud backup services play a critical role in modern data protection, offering reliable and scalable options for safeguarding against data loss. With features like automated backups, encryption, cross-platform compatibility, and disaster recovery capabilities, these services ensure data integrity, accessibility, and security across varied devices and locations. By adopting effective backup strategies—such as incremental, differential, and mirror backups—organizations can optimize both data recovery speed and storage efficiency.
See Additional Guides on Key Data Breach Topics
Together with our content partners, we have authored in-depth guides on several other topics that can also be useful as you explore the world of data breaches.
Ransomware Protection
Authored by N2W
- [Guide] Ransomware Protection: 7 Defensive Measures
- [Guide] Ransomware Prevention: 11 Ways to Prevent Attacks
- [Product] N2WS | Cloud Backup and Restore
Data Protection
Authored by Cloudian
- [Guide] What is Data Protection and Privacy?
- [Guide] Keeping Up with Data Protection Regulations
- [Whitepaper] Forrester Report – Protection from Ransomware Attacks
- [Product] Cloudian | Enterprise-Class, S3-Compatible Object Storage Software
Disaster Recovery
Authored by Imperva
- [Guide] IT Disaster Recovery Solutions | Components & Challenges
- [Guide] Business Continuity & Disaster Recovery Planning (BCP & DRP)
- [Blog] What’s Different About Data Security in the Cloud? Almost Everything
- [Product] Imperva Account Takeover Protection | Secure and Effective Account Takeover Protection
