Why Should You Back Up AWS EC2 Instances?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a cloud computing service that provides resizable compute capacity in the cloud. It allows users to launch virtual servers, known as instances, which can be configured with various operating systems, memory, and storage options.
As EC2 becomes used for large scale, mission critical applications, backing up data regularly becomes critical. Backups should be implemented properly and tested often, so that if a disaster occurs, the business doesn’t suffer.
Taking a backup of your AWS resources frequently is very important in order to be able to recover from a disaster. It’s important to schedule AWS backups on a timely basis, such as taking backup weekly or monthly on different availability zones.
This is a part of articles about AWS Backup.
What Is the Difference Between AWS EC2 Snapshot and Backup?
An EC2 snapshot (also known as EBS snapshot) is a point-in-time copy of an EBS volume, which is attached to an EC2 instance. Snapshots capture only the changes made since the last snapshot, making them incremental and space-efficient. They are typically used for creating backups of specific EBS volumes, restoring volumes, or creating new volumes based on existing data. Snapshots are stored in Amazon S3, and you can create new EBS volumes from snapshots to restore data or replicate instances in different regions or availability zones.
AWS Backup is a fully managed service that allows you to automate and centralize the backup of your AWS resources, including EC2 instances, databases, and file systems. AWS Backup simplifies the backup process by offering a unified, policy-based framework to define backup schedules, retention periods, and compliance requirements across multiple AWS services. While EC2 snapshots focus on individual EBS volumes, AWS Backup provides broader coverage, enabling the protection and recovery of entire EC2 instances, including attached volumes and AMIs.
In the past, it was common to create a new Amazon Machine Image (AMI) from an existing instance or a snapshot, as an alternative to capturing an EBS snapshot. Most of the modern techniques and recently introduced tools, including the ones discussed below, focus on backing up EBS volumes alone.
4 Different Ways to Take EC2 Instance Backups
1) N2WS Backup & Recovery Tool
N2WS Backup & Recovery is a cloud-native tool to back up, restore, and optimize the data lifecycle for your AWS resources. Using it, you can automate backups for one or more AWS accounts from a single pane of glass, simplifying the backup process and making it a great tool when dealing with disaster recovery, compliance requirements and storage savings.
See how to automate EC2 instance backups in 1 minute 👇 or click around a tour.
N2WS allows users to manage multiple AWS accounts and configure policies and schedules to take automated snapshot backups. It also has a Windows agent to consistently back up Windows applications without the need for maintenance windows. Furthermore, in a dynamic cloud environment, you need to be able to keep consistent backup policies across all your instances at any point in time.
Using EC2 instance tags, N2WS can automatically assign each one of these new instances the appropriate backup policy based on their purpose and your initial configuration. For more info, check out our previous article about tag-based continuous AWS cloud backup.N2WS’ latest versions have several features specifically designed to save on your monthly AWS bill such as Resource Control, an instance scheduler to start/stop instances on-demand for better control of your resources particularly when they are idle. Also, with N2WS, you can automatically archive data into longer term storage, resulting in reduced storage costs—up to 98%.
- Use cross-region replication for disaster recovery: Instead of just relying on multi-AZ backups, consider replicating snapshots to a different AWS region. This ensures that even in the event of a regional outage, your data remains recoverable.
- Test restores regularly: Automated backups mean little if you don’t regularly test the recovery process. Schedule quarterly or bi-annual full instance restores to ensure that your backups are functional and meet recovery time objectives (RTOs).
- Tag resources consistently: In environments with hundreds of EC2 instances, tagging consistency (e.g., using tags like “Environment: Production” or “App: Database”) helps in applying backup policies more efficiently using tools like AWS Data Lifecycle Manager (DLM).
- Leverage custom retention policies: Instead of using default retention periods, tailor retention policies based on the criticality of the data. For example, keep hourly snapshots for 24 hours, daily for a week, and monthly for a year.
- Monitor snapshot storage costs: Regularly review AWS Cost Explorer to monitor snapshot storage costs, particularly when dealing with cross-region or long-term retention.
2) Automate Backups Using AWS Data Lifecycle Manager
In July of 2018, Amazon released Data Lifecycle Manager (DLM), a tool for automating EBS volumes. DLM allows you to use tag-based lifecycle policies to define various backup schedules.
To get started, open LifeCycle Manager under the EC2 instance service and start defining the policy.
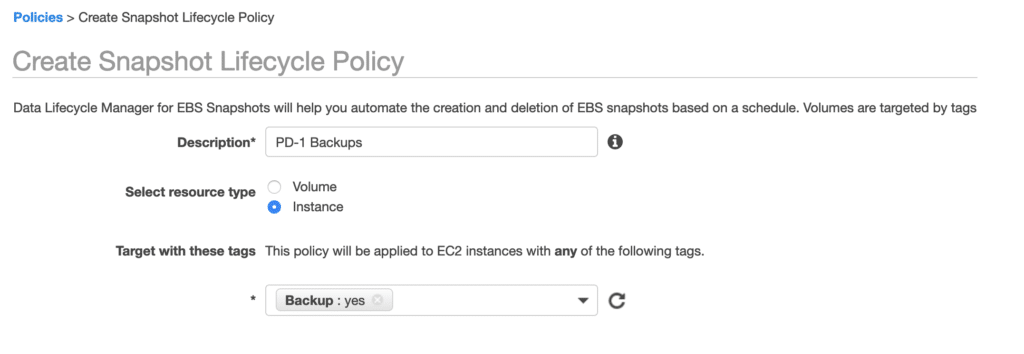
Policy works by looking at the desired tags, so make sure your resources are tagged properly before starting. You can also pick the resource type. This is helpful when you only want to look for tagged EBS volumes, rather than finding all the tagged EC2 instances.
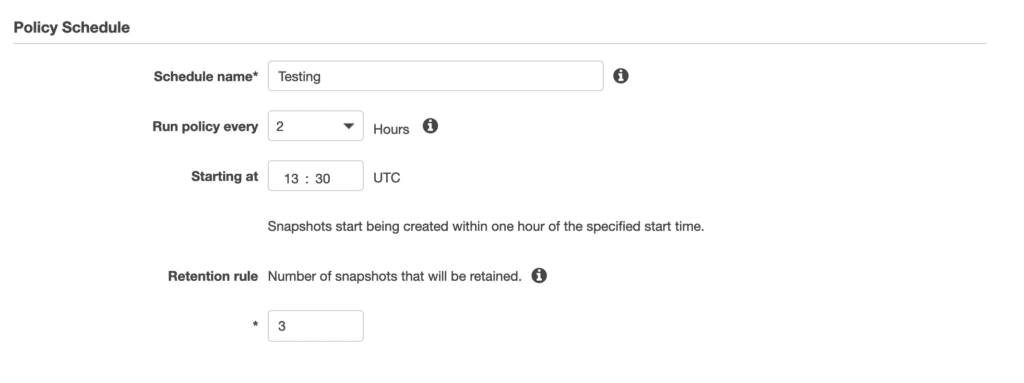
Further down, you define the backup schedule. Simply choose the starting time and how often the policy will run (you can choose between 2h and 24h). You will also need to pick the number of snapshots to be retained.
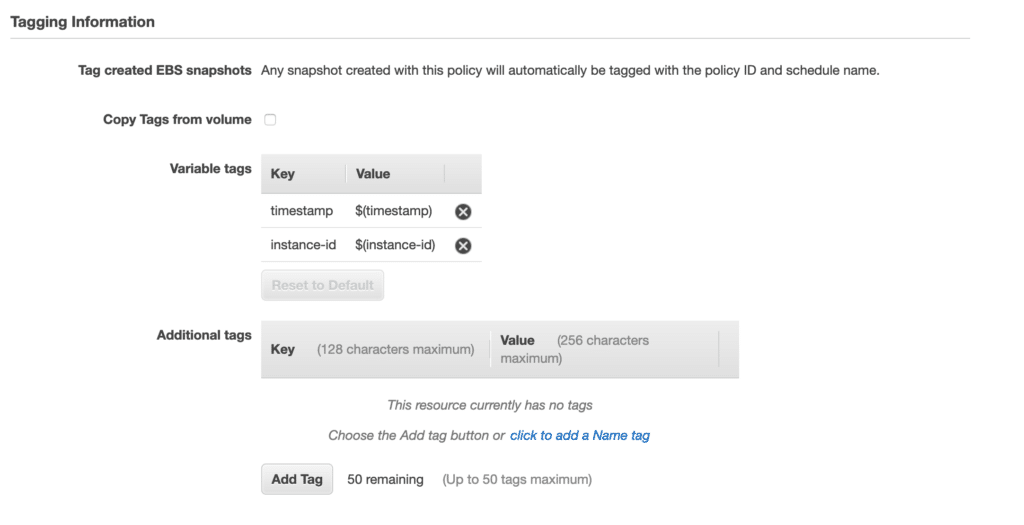
You can have additional tags added to your snapshots, either by checking the option to copy the tags from the original volume or by adding new ones yourself.
You can also exclude the snapshot of the root volume. This is a useful option if you only need additional data volumes to be backed up. For the role, you can keep the default.
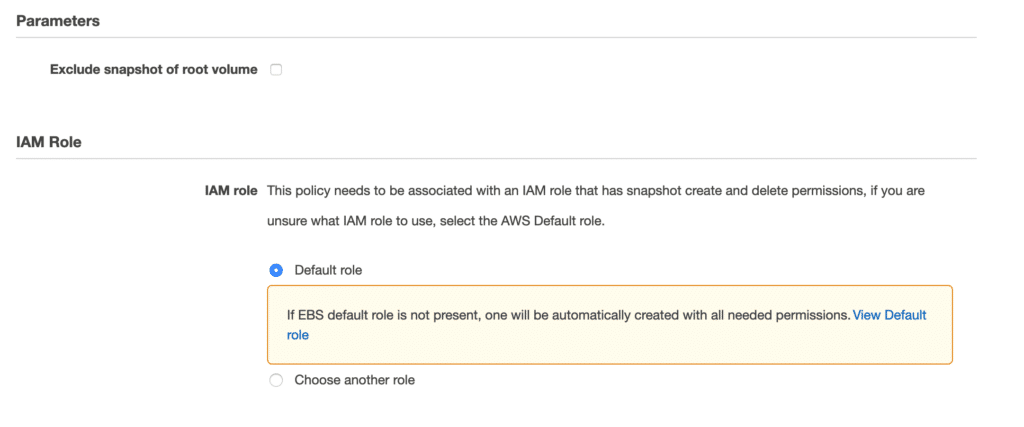
It is possible to create the policy without immediately enabling it. If you do this, simply modify the policy later.
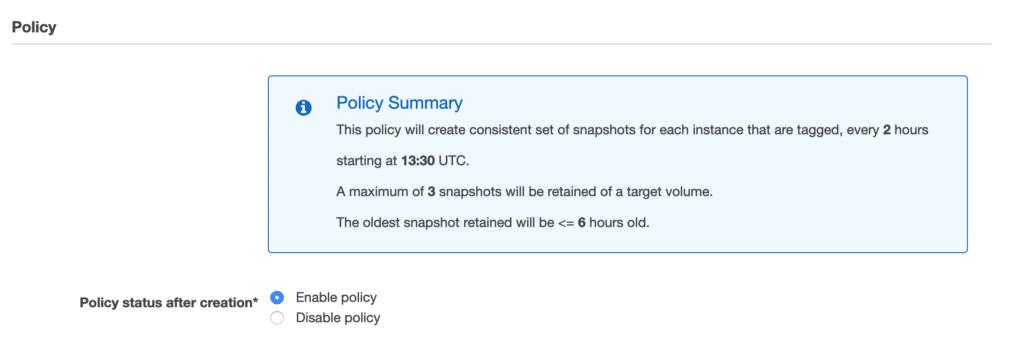
After you are done, you can see your newly created policy, as well its status.
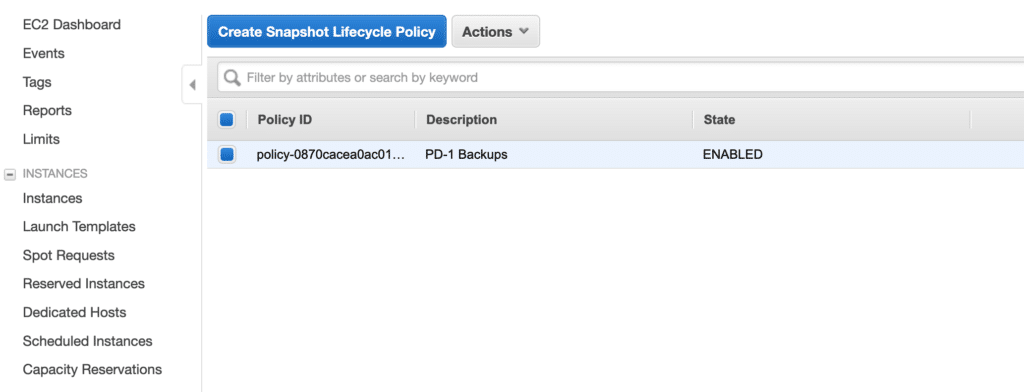
If you want more details, you can look at the policy summary. It will tell you exactly how you have defined the backup schedule, and it will show the retention of the backups.

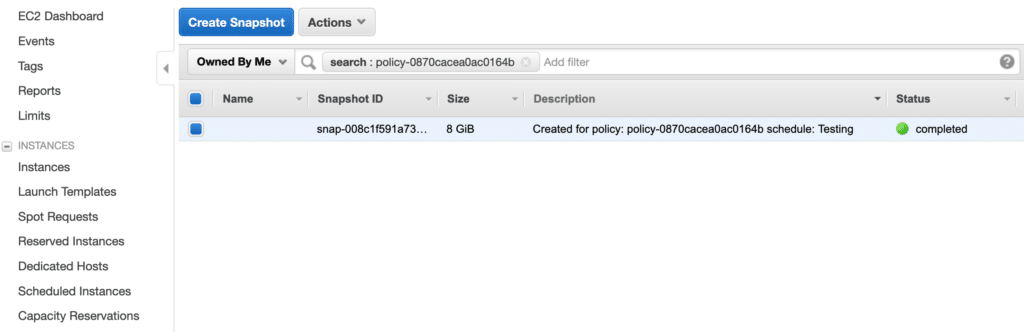
When the defined schedule triggers backups, you will see them under Snapshots.
3) Backup Automation Using AWS Backup
AWS Backup is a fully managed service that is used to automate backups on AWS (though it can be implemented on-premises as well, by using AWS Storage Gateway). Compared to Data Lifecycle Manager, it is a much more powerful tool, and it can serve as a centralized location for configuring and monitoring backups.
AWS Backup can be used not only for an EBS volume, but also for RDS databases, DynamoDB tables, Storage Gateway volumes, and even EFS file systems.
To start, open the AWS Backup service.
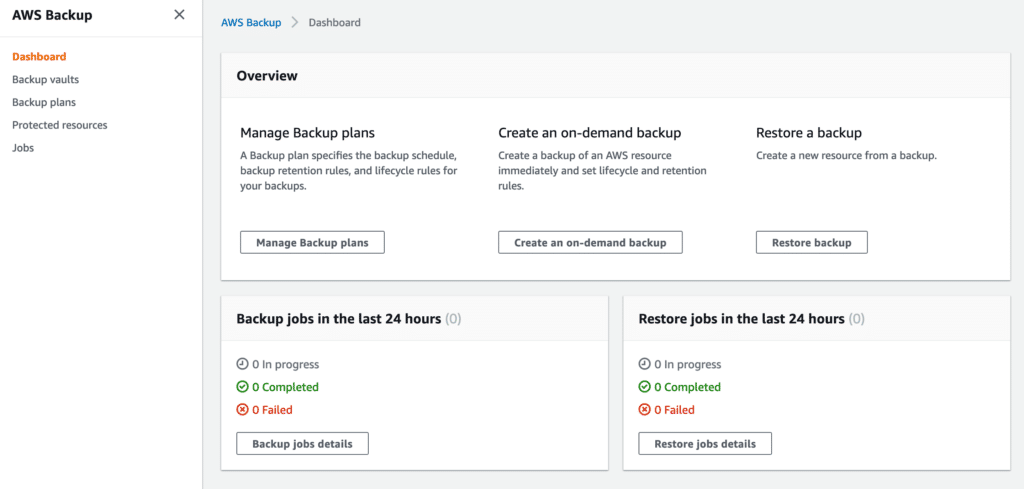
Click on Backup plans (or Manage Backup plans), and then Create Backup plan.
There, you have a couple of options.
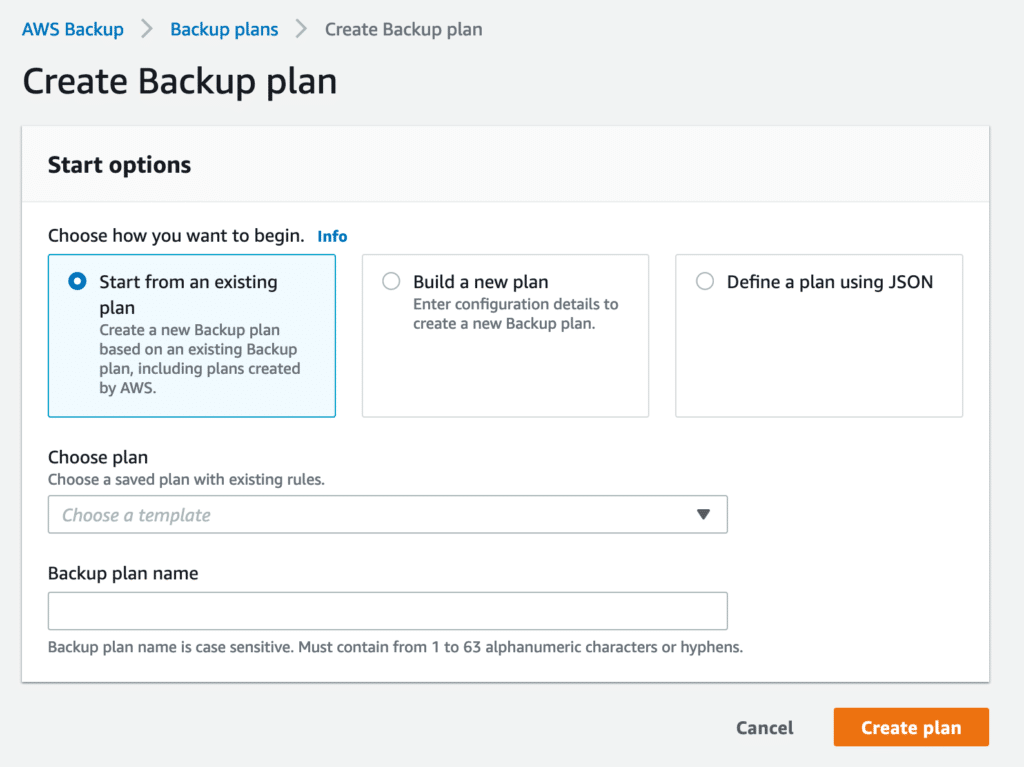
You can start by using an existing plan and choosing an option such as “Daily 35-day retention” or “Daily Monthly 1yr Retention.” In this example, we are going to start from scratch, so pick Build a new plan.
After naming your plan, you will configure the backup rule—or, more specifically, a schedule that will be followed for creating backups. Make sure you set the desired backup window (if using a custom one, UTC is always used and can’t be changed) and the frequency of execution.
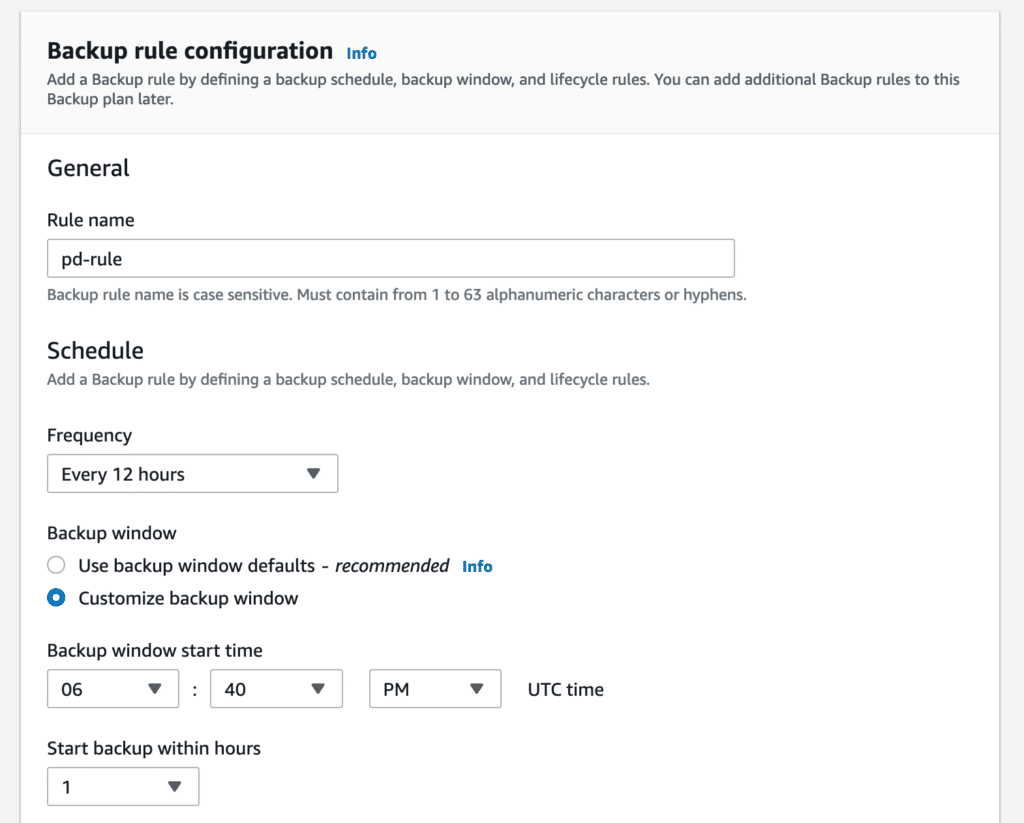
You can also create the life cycle settings and either transition the backups to Amazon Glacier cold storage or expire them completely.
Below that section is the one in which you pick the Backup vault. You can either use the default one or select a custom vault, if you’re looking for logical separation. As with the Data Lifecycle Manager, you can add tags to your backups if needed.
After you’re done and your plan is created, it is time to assign resources to it.
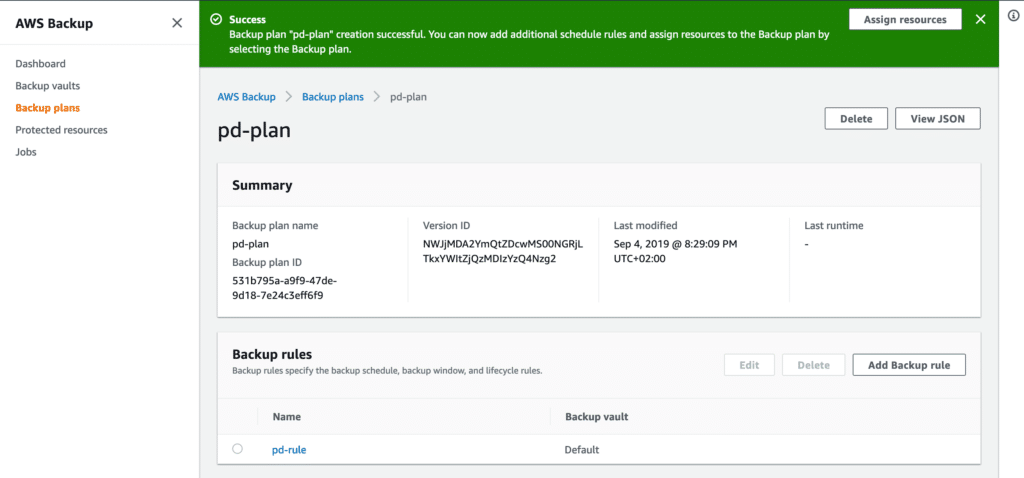
Resources can be assigned by using tags or by adding them based on the Resource ID.
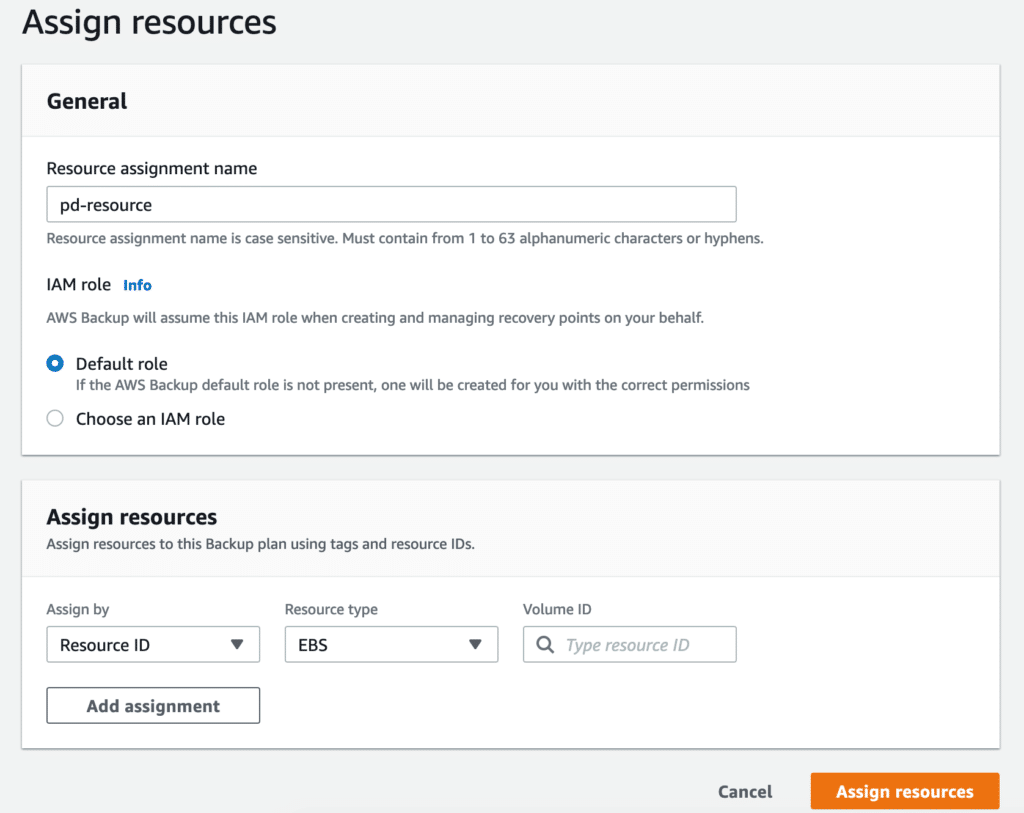
With the plan created and the resources assigned, your AWS Backup is ready.
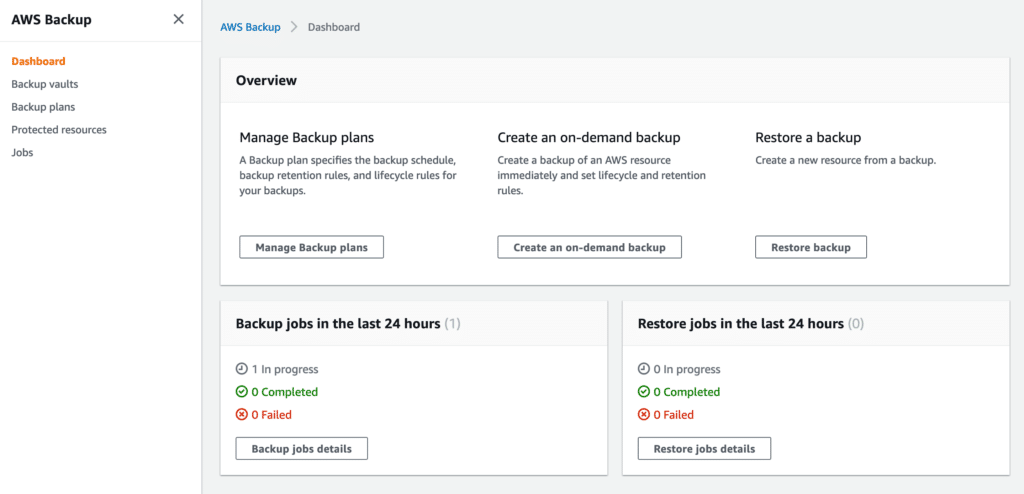
You can go back to the AWS Backup dashboard and actually see the backup (and also restore) jobs. The screenshot below shows that there is a backup job in progress.
After the backup has been completed, the dashboard will be updated accordingly, as shown below.
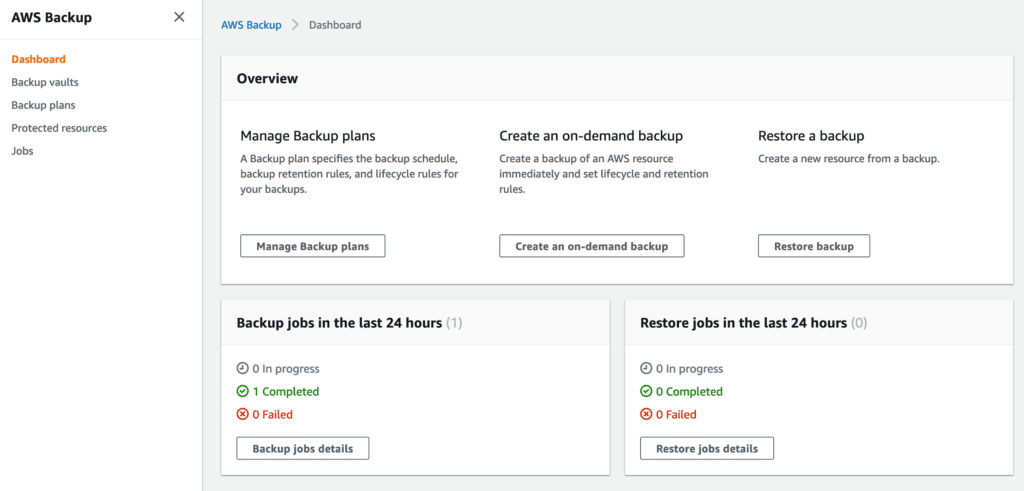
With AWS Backup, you can easily initiate the restore of your backups. This can be very convenient, especially in a disaster recovery situation when multiple volumes may need to be restored quickly.
4) Schedule Automated Amazon EBS Snapshots Using CloudWatch Events
The last backup method we will examine is EBS Snapshot creation using CloudWatch events. To implement this process, you will use a CloudWatch rule.
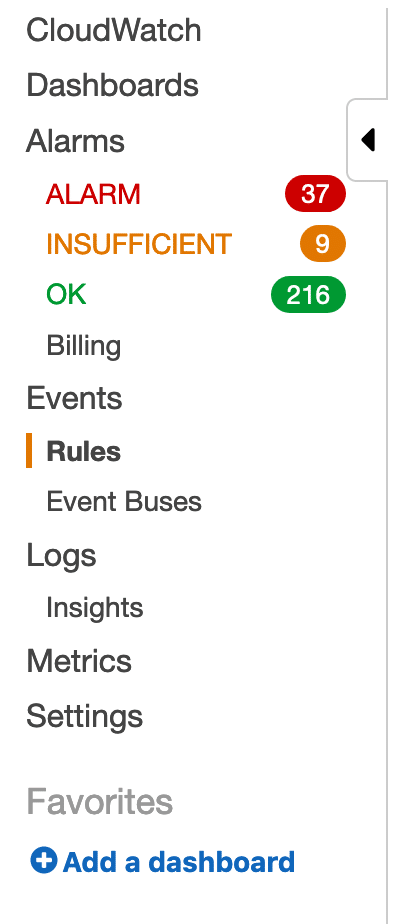
Click on Create rule, and pick Schedule under Event Source.
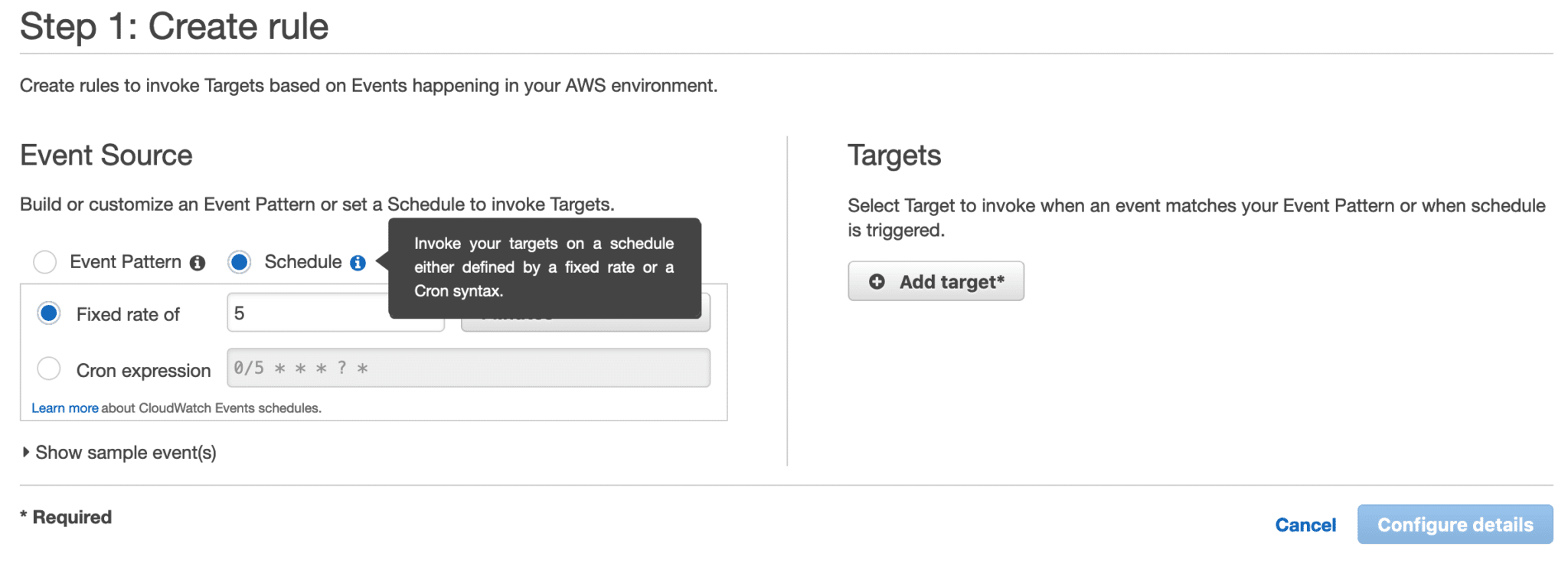
This will give you two options: you can either have this rule triggered using a fixed rate (every X minutes, hours, or days), or you can use a cron expression, which gives you much more flexibility. For example, you can have an event that triggers every Wednesday, Thursday, and Friday at 6pm. You will also see a preview of your next ten trigger dates. Do note that all times are presented in GMT.
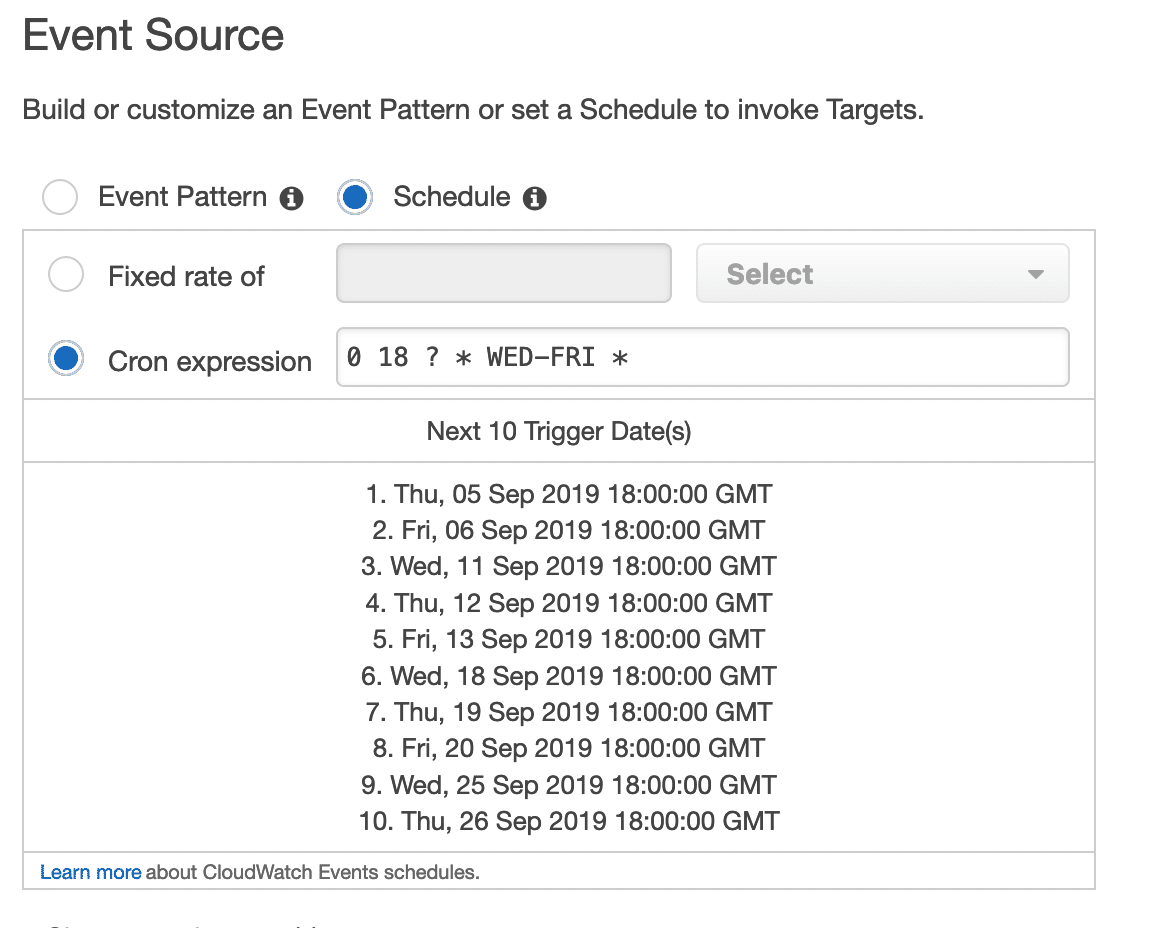
After configuring the desired schedule, click on Add Target and chose “EC2 CreateSnapshot API call” from the list. Then, copy the volume ID of the volume you want to backup. You can leave the option to create a new role, unless you have one already.
Click on Configure details, name your rule, and give it description. After that, you are ready to go.
Automating AWS EC2 Backup is a great way to save time and ensure critical data is protected
AWS EC2 backup automation is a great way to save time on recurring tasks. It also helps you to confirm that desired tasks have indeed been done. Since having regular backups is an absolute must in any business environment, this critical process should be not hinge upon manual execution.
Depending on your cloud environment, one of the four different methods presented above for automating your AWS EC2 instance backups could be a better fit than the others. N2WS Backup & Recovery is worth exploring, since it is a powerful and useful tool, as it supports not only AWS EC2 instance backup, but a range of other AWS services such as RDS, Redshift, DynamoDB, Aurora, and EFS all under one single pane of glass.You can manage your entire AWS backup and recovery operations from a dedicated N2WS instance within your secure AWS environment as you scale. You can check it out by spinning up a 30 day free trial here (no credit card needed). Bonus: your free trial automatically turns into our forever Free Edition.
