What Is Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager?
Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager (DLM) is a native AWS service to automate the management of Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) snapshots and EBS-backed Amazon Machine Images (AMIs). Its purpose is to define lifecycle policies that schedule creation, retention, and deletion operations on these storage resources.
DLM is useful for organizations implementing regular backup strategies across multiple AWS resources while maintaining control over storage costs and data integrity. The service supports large environments and high resource volumes.
However, the DLM service also has notable constraints. Policies are rigid: changing a tag or schedule can orphan older snapshots, leaving them unmanaged and incurring costs. Backup timing lacks precision, as snapshot creation can be delayed by almost an hour, making it unsuitable for workloads needing strict recovery point objectives. The service also does not natively support cross-zone replication, requiring custom automation for broader disaster recovery.
This is part of a series of articles about AWS backup
In this article:
- Key Features of AWS Data Lifecycle Manager
- How AWS Data Lifecycle Manager Works
- Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager: Pros and Cons
- Tutorial: Create AWS Data Lifecycle Manager Policy for EBS Snapshots
- Best Practices for AWS Data Lifecycle Manager
Key Features of AWS Data Lifecycle Manager
Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager provides an automated, policy-driven approach to managing EBS snapshots and EBS-backed AMIs:
- Automation: Policies can be customized to create, retain, and delete backups on a fixed schedule or via cron expressions.
- Visual interface: The service integrates with a graphical interface, making it easier to configure and manage without specialized training.
- Backup capabilities: It supports application-consistent backups by allowing pre- and post-scripts to pause and resume I/O operations. These can be sourced from AWS Systems Manager documents or custom scripts for applications such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, SAP HANA, InterSystems IRIS, EHR systems, and Windows workloads.
- Security monitoring: Policies can also be monitored through Amazon CloudWatch, with metrics for creation, deletion, and copying activity, as well as alarms for threshold breaches.
- Compliance and disaster recovery: DLM offers account-level default policies, supports snapshot copying to isolated accounts, and meets SOC, PCI, FedRAMP, ISO, and HIPAA eligibility requirements. It automatically deletes expired snapshots and deregisters outdated AMIs.
- Management options: The service allows management via the AWS Management Console, CLI, SDKs, Terraform, or CloudFormation. Policies can target single EBS volumes, groups of volumes, or entire EC2 instances, and can include encryption with alternate AWS KMS keys for additional security in cross-account copies.
How AWS Data Lifecycle Manager Works
Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager operates through policies that define when and how EBS snapshots or EBS-backed AMIs are created, retained, and deleted. Each policy specifies the resource type it manages, the target resources, the creation frequency, the retention period, and any additional actions such as cross-Region copying, archiving, or tagging. Policies can be either default or custom.
Default policies apply at the account level to all resources in a Region that lack recent backups. You can exclude specific volumes or instances through exclusion parameters. There are two types: one for EBS snapshots, which targets volumes, and one for EBS-backed AMIs, which targets instances. Each account and Region can have only one default policy per resource type.
Custom policies use resource tags to target specific volumes or instances. They support features such as fast snapshot restore, cross-account copying, snapshot archiving, and pre/post scripts for application-consistent backups. A custom policy can have up to four schedules, each with its own frequency, retention settings, and feature configuration.
In custom policies, multiple schedules within the same policy can produce snapshots or AMIs at different intervals—daily, weekly, monthly, or yearly—while avoiding duplicate backups when schedules overlap. In such cases, the highest retention period and combined tags are applied to the resulting backup. Target resource tags determine which resources are included. Any resource that has at least one matching tag key-value pair will be backed up. Policies can be combined by assigning multiple tags to the same resource.
When creating snapshots, DLM uses incremental backups to reduce storage costs—only changed data since the last snapshot is stored. For EBS-backed AMIs, the service creates snapshots for all attached EBS volumes of the source instance. System-generated tags are applied to identify policy ID, schedule name, expiration time, archival status, and whether pre- or post-scripts were used. You can also apply your own custom tags at creation, and optionally propagate target resource tags to the backups.
Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager: Pros and Cons
Before adopting Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager, it’s important to understand its strengths and limitations. While it offers significant automation for EBS snapshot and AMI management, certain design constraints and operational quirks can affect its suitability for specific environments.
Pros
- Simple setup: A policy can be deployed with just a JSON file containing the resource type, target tag, and schedule, plus an IAM role granting create/delete snapshot permissions.
- Storage efficiency: Uses incremental backups so only changed data is stored, reducing space and costs.
- Built-in monitoring: Integrates with Amazon CloudWatch for tracking snapshot creation and policy status.
Cons
- Policy changes leave old snapshots unmanaged: If target tags or schedule names change, snapshots created under the previous settings are no longer maintained, potentially leading to unmanaged resources and extra costs.
- Timing is approximate: Snapshot creation can start up to 59 minutes after the specified time, which may be unsuitable for precise backup windows.
- No built-in cross-zone replication: an EBS volume is tied to a single Availability Zone, so cross-zone or cross-Region copies require custom scripts for disaster recovery.
- Policy limit constraints: Multiple policies are needed to run multiple backup schedules on the same volume, which can add complexity and risk hitting per-Region policy limits.
While AWS DLM works well for basic snapshot automation, enterprises quickly outgrow its limitations. That’s where N2W extends AWS-native capabilities: flexible, tag-driven policies that won’t orphan snapshots, instant recovery (rather than “within the hour”), and seamless cross-account or cross-cloud backup.
Tutorial: Create AWS Data Lifecycle Manager Policy for EBS Snapshots
Follow these steps to create a default policy for Amazon EBS snapshots:
Step 1: Set up a new policy
Go to https://console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/ and sign in to your AWS account.
In the left navigation pane, choose Lifecycle Manager, then select Create lifecycle policy.
Under Policy type, choose Default policy. Select EBS snapshot policy.
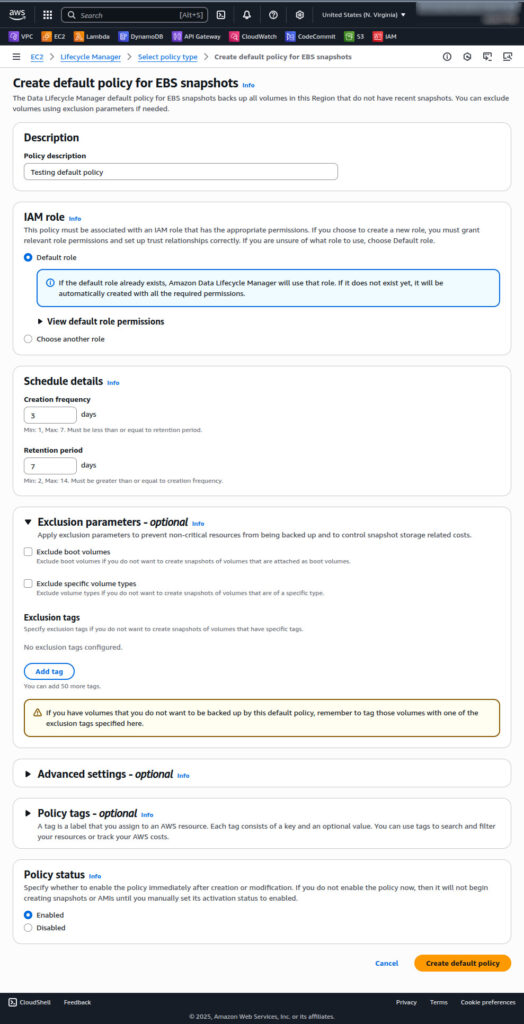
Enter a brief description to identify this policy. Select the IAM role that has permissions to manage snapshots.
You can use the default role AWSDataLifecycleManagerDefaultRole or a custom role. Specify how often snapshots should be created (creation frequency). The policy only backs up volumes that haven’t been backed up by any other method within this interval.
Example: A 3-day frequency will skip volumes backed up within the last 3 days.
Step 2: Set the retention period
Enter how long snapshots should be retained before deletion. This must be equal to or longer than the creation frequency.
Step 3: Configure exclusion parameters (Optional)
Exclude boot volumes to back up only non-boot data volumes. Exclude specific volume types by selecting them from the list. Exclude by tags by specifying tag key-value pairs. Volumes with matching tags are skipped.
Step 4: Adjust advanced settings (Optional)
Copy tags from source volumes to snapshots. Enable extend deletion to remove all snapshots, including the last one, if the volume is deleted or the policy is disabled.
Enable cross-Region copy to send snapshots to up to three Regions. Encryption settings follow the source and destination Region defaults.
Step 5: Add tags to the policy (Optional)
Add custom tags to help identify and manage the policy. Choose Create default policy to save and activate the snapshot lifecycle policy.
Best Practices for AWS Data Lifecycle Manager
Here are some useful practices to consider when using AWS DLM.
1. Use Descriptive Naming for Policies
Clear and descriptive naming conventions for Data Lifecycle Manager policies improve operational clarity in environments with many resources and policies. Using structured names—such as including compliance scope, resource type, and environment (e.g., “prod-database-daily-snapshots”)—makes it easier to identify the purpose and coverage of each policy at a glance. This is important during audits, policy reviews, and incident investigation.
Descriptive names aid collaboration across teams by making policies self-explanatory, lowering the barrier for new team members and auditors to understand policy intent. They also make it easier to automate operations involving policies through scripts or Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) solutions. Consistent naming approaches help prevent policy sprawl and duplication.
2. Define Multiple Schedules Within a Single Custom Policy
AWS DLM supports creating custom policies that include multiple schedules, each with its own frequency and retention rules. By consolidating schedules in one policy, teams can manage distinct backup needs for different workloads or compliance requirements on the same set of resources. For example, a policy could enforce frequent, short-term backup cycles and less frequent, long-term retention.
Multiple schedule support simplifies lifecycle management and aligns backup operations with complex business requirements, such as financial data needing both daily and monthly retention. Reviewing and managing a single policy with multiple schedules reduces policy sprawl and makes maintenance more efficient.
3. Regularly Review and Prune Unused Policies
Regular reviews of Data Lifecycle Manager policies are essential to prevent outdated, redundant, or unused configurations from persisting in your AWS environment. Over time, teams might accumulate policies targeting decommissioned workloads or old resource tags, resulting in unnecessary or failed snapshot operations. Reviewing policies periodically ensures they remain aligned with current environments and operational needs.
Pruning unused or obsolete policies also improves security by minimizing the attack surface. Stale policies can lead to confusion during incident response or audits, increasing the chance of errors. Automated tools or scripts can assist in identifying policies with no recent activity or associated resources, making cleanup more manageable.
4. Implement Application-Consistent Backups
Application-consistent backups go beyond simple volume snapshots by ensuring the application data is in a reliable, recoverable state. Using AWS DLM’s support for lifecycle hooks, you can invoke scripts to quiesce applications before a snapshot and resume operations after. This approach protects against issues like truncated transactions or incomplete writes that can arise from crash-consistent (raw volume) snapshots, particularly for databases or transactional systems.
Configuring DLM policies for application consistency requires additional setup, such as custom Lambda functions or using AWS Systems Manager Run Command for pre- and post-snapshot operations. Always document these procedures as part of your recovery plan, and periodically test recovery from application-consistent backups to validate data integrity and process reliability.
5. Use Cost Analytics Tools for Visibility
Storage costs for EBS snapshots and AMIs can escalate quickly in large or dynamic environments. AWS provides built-in cost analytics tools like AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets, which can be configured to track and break down backup-related costs. By tagging resources and policies consistently, you gain detailed visibility into backup spend, identify costly retention policies, and monitor trends over time, enabling proactive cost optimization.
Integrating cost reporting into your DLM workflows helps enforce budget adherence and supports ongoing optimization efforts. You can set cost or usage alerts to notify teams about unexpected spikes, and analyze snapshot age and volume to identify candidates for pruning. Leverage tagging strategies and reporting dashboards for maximum clarity and control.
How N2W Automates (and Improves on) DLM
Think of AWS Data Lifecycle Manager as a solid starting point—it’s the training wheels for snapshot automation. But when your environment grows, training wheels don’t cut it. That’s where N2W takes over, delivering the speed, flexibility, and cost savings enterprises actually need.
Here’s how N2W builds on (and goes beyond) AWS DLM:
- Ridiculously precise scheduling: DLM only promises snapshots within the hour—which isn’t great if your compliance or RPO targets are strict. With N2W, you can schedule backups down to the exact minute, with 60-second precision. Your backups run exactly when you need them, not “whenever AWS gets around to it.”
- Cross-account and cross-cloud resilience: Don’t just back up across Regions—restore into another account, or even into Azure or Wasabi, with immutability baked in. It’s like putting your data in a secret vault no one can touch, not even you.
- Rapid recovery, no waiting game: DLM snapshots might take up to an hour. With N2W, you can spin up full servers, VPCs, or just a single file in seconds, orchestrating complete failovers or granular restores with just a few clicks.
- Air-gapped + immutable protection: Create a true “hands-off” disaster recovery account where nobody—not ransomware, not human error—can delete your backups. Add MFA, encryption, and automated alerts, and sleep easy at night.
- Serious cost savings baked in: With AnySnap Archiver, N2W ingests your existing snapshots and archives them instantly—cutting storage bills by up to 98%. You can even schedule unused resources to power down nights and weekends and save another 50%.
In short, DLM gives you the basics. N2W gives you enterprise-grade protection, automation, and cost optimization—all in one console.
👉 Want to slash your AWS backup costs while getting faster, safer recovery?
Download our free AWS Cost Savings Guide and see how top enterprises are saving millions.
