What Are Azure Backup Services?
Azure Backup Services provide scalable and secure solutions for protecting and restoring data stored in Microsoft Azure, or using Microsoft Azure to backup systems running on-premise or in other clouds. Azure Backup Services help organizations protect critical workloads, applications, and virtual machines by enabling efficient data recovery.
Azure Backup Services typically provide capabilities like automated backup scheduling, customizable retention policies, and encryption for data security. As these services integrate with the Microsoft Azure ecosystem, they are also well-suited for hybrid cloud environments, offering cost-effective and reliable data protection.
In this article
- Key Features of Azure Backup Services
- Third-Party Azure Backup Services
- First-Party Azure Backup Services
Key Features of Azure Backup Services
Azure Backup Services offer a framework for protecting data across cloud-native and hybrid environments:
- Integration with Azure resources: Built-in support for backing up Azure virtual machines, Azure Files, Azure SQL Database, and other native services, with configuration managed directly from the Azure portal.
- Granular and policy-based management: Backup policies can be defined by resource type, location, or business unit, enabling fine-grained control over backup schedules, retention periods, and compliance alignment.
- Backup for on-premises workloads: Azure Backup Server and Azure Arc allow on-premises Windows and Linux systems to be backed up to Azure, supporting hybrid and phased cloud migration strategies.
- Data lifecycle and tiering options: Users can move older backup data to archive storage tiers for cost savings, while keeping recent backups in hot or cool tiers for faster access.
- Security and compliance features: Features like encryption, multi-factor authentication, soft delete, and immutable backup support help meet regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001.
Third-Party Azure Backup Services
Here are some of the leading Azure backup solutions provided by third-party vendors on top of Azure infrastructure.
1. N2W
N2W Backup for Azure is a cloud-native data protection solution designed to deliver reliable backup, rapid recovery, and cross-cloud disaster recovery for AWS and Azure workloads. N2W provides snapshot-based backups, cross-region and cross-subscription automated backup and restore along with automated archival tiering to Azure Blob storage. Its flexible architecture enables fast VM recovery and non-disruptive disaster recovery testing while maintaining cost efficiency and transparent pricing. Although originally known for its deep AWS integration, N2W now extends robust support to Azure environments, giving organizations centralized control over multi-cloud backup and cross-cloud restore operations with secure, scalable protection.
Key features include:
- Snapshot-Based Azure Backup: Utilizes native Azure snapshot APIs to create fast, application-consistent backups without requiring agents or additional infrastructure.
- Cross-Region and Subscription Recovery: Enables rapid recovery of Azure VMs across regions or subscriptions, supporting high availability and business continuity.
- Cross-Cloud Backup & Recovery: Enables automated backup and rapid recovery of Azure VMs across multiple cloud providers (AWS, Azure and Wasabi) for the ultimate defense against cyber threats, cloud power outages and vendor lock-in.
- Policy-Driven Automation: Automates protection of Azure resources based on tags, groups, or schedules, simplifying backup management at scale.
- Disaster Recovery Testing: Facilitates non-disruptive DR testing by launching isolated copies of backups, ensuring compliance-readiness and recovery validation.
- Centralized Multi-Cloud Management: Manages backup and recovery across both Azure and AWS from a unified interface, ideal for hybrid or multi-cloud operations.
- Long-Term Cost Optimization with Blob Storage Tiering: Automatically copy backup data to cold Azure Blob tiers based on retention policies, significantly reducing storage costs over time while meeting compliance and archival requirements.
2. Veeam Backup for Microsoft Azure

Veeam provides a policy-based backup solution for Microsoft Azure workloads. It supports full and granular recovery, automation, and secure access controls across cloud and hybrid environments.
Key features include:
- Immutable backup storage: Uses Azure Blob with WORM settings to prevent backup modification or deletion.
- Policy-based automation: Automatically discovers and protects resources based on defined backup policies.
- Granular recovery options: Enables restoration at the VM or file level, including cross-region and cross-subscription recovery.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud support: Works with Veeam Backup & Replication for consistent protection across environments.
- Least privilege access control: Implements RBAC and identity policies to enforce minimal access permissions.
Limitations of Veeam:
- Limited deployment options: Deployment of Veeam Backup for AWS is restricted to CloudFormation templates, offering less flexibility compared to solutions that support manual deployment or custom naming conventions.
- Complex backup configuration: Setting up backup policies is not user-friendly and often requires tagging resources, making it difficult to exclude specific volumes without in-depth knowledge of the infrastructure.
- Lack of multi-tenancy: The solution does not support multi-tenancy, limiting its use for MSPs who need to provide separate backup consoles for individual clients.
- Outdated terminology: Veeam uses on-premise terminology for cloud solutions, such as referring to backups as “replicas,” which can confuse users accustomed to modern cloud terminology.
- Recovery limitations: The recovery process is cumbersome, requiring users to know specific resources for restoration, as policies are not searchable or linked to the recovery workflow.
- File-level recovery concerns: File and folder-level recovery allows restoring to the same instance, raising potential security risks as this access could inadvertently introduce malware.
- Immutability gaps: Veeam does not support immutable EBS snapshots for AWS but does offer S3 object lock for certain storage classes. However, it lacks support for cost-efficient options like S3 Infrequent Access.
- Ineffective cost estimation: The cost estimation tool for archives often provides inaccurate calculations due to its inability to account for all variables, reducing its utility for budget planning.
- Inefficient cleanup: Unused backups can only be cleaned up once daily, potentially leading to unnecessary storage costs until the next cleanup cycle.
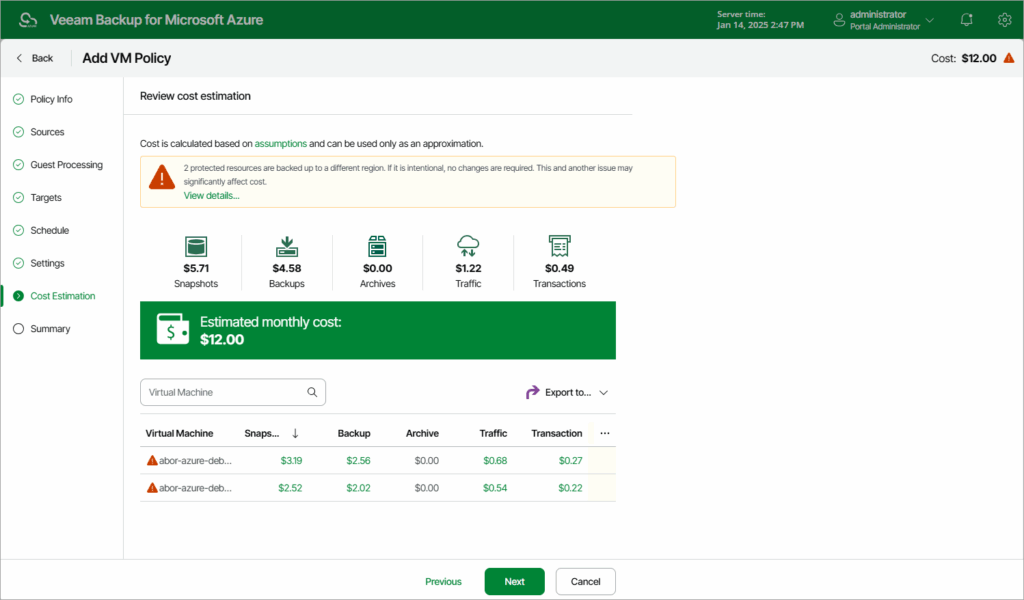
Source: Veeam
3. Rubrik Data Backup for Azure
Rubrik offers a cloud-native solution to manage data protection across Azure workloads. It includes automated policies, native integrations, and centralized control for multi-region deployments.
Key features include:
- Native Azure integration: Protects services like Azure VMs, Managed Disks, and SQL using native snapshot APIs.
- Immutable snapshots and air-gapped storage: Stores backups in WORM-locked Azure Blob within logically isolated environments.
- Centralized management across environments: Consolidates control of multiple regions and resource groups through a single platform.
- Predictive search and fast recovery: Supports file-level and full workload recovery using search and crash-consistent snapshots.
- Automated policy-based protection: Applies SLA-based backup policies by tagging or grouping Azure resources.
Limitations of Rubrik (as reported by users on G2):
- UI inconsistencies and usability issues: Users reported that the interface could be confusing and sometimes inconsistent across modules, making it harder to perform tasks quickly.
- Limited reporting and customization: The reporting functionality lacks depth and does not provide customizable dashboards, which makes compliance and audit tracking more difficult.
- Slow support response times: Some users experienced delays in getting support, especially for complex technical issues that required escalation.
- Complexity in initial setup: The onboarding and initial configuration process can be time-consuming and may require significant technical expertise to align with organizational policies.
- Lack of granular backup options: Users noted that there is limited flexibility in choosing files or folders for backup within a workload, which may lead to inefficient use of storage.
Source: Rubrik
4. Acronis Backup for Azure

Acronis provides a unified platform that combines backup and cybersecurity capabilities for Azure virtual machines. It focuses on simple management, fast recovery, and threat prevention.
Key features include:
- Agentless backup for Azure VMs: Protects workloads without installing agents to reduce complexity.
- Recovery with Acronis Instant Restore: Supports fast recovery of VMs to reduce downtime.
- Integrated cyber protection: Offers ransomware protection and malware defenses using AI-based detection.
- Immutable and encrypted backups: Uses AES-256 encryption and immutability to secure backup data.
- Flexible storage options: Allows storage across Acronis Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, private clouds, or local storage.
Limitations of Acronis:
- Limited customer support on weekends: Users have reported dissatisfaction with the lack of support during weekends, a critical period for many organizations performing Azure disaster recovery (DR) tests or backups.
- Complex access control: The technical documentation for configuring access control is not well-explained, leading to challenges in implementation and administration.
- Inconsistent onboarding: Some users experienced issues during onboarding due to changes in account representatives and unclear credit and setup processes.
- Overwhelming product range: While Acronis offers a broad suite of features, the learning curve can be steep. The partner portal includes resources, but best practices can be challenging to interpret without additional guidance.
- Non-intuitive interface: Setting up backups, especially selecting files and folders, can be cumbersome. Users must rely on third-party tools like TreeSize to estimate folder sizes, which adds to setup time.
- Inefficient backup connection process: When connecting an old backup to a new PC, the process can be lengthy and error-prone, potentially resulting in wasted storage space.

Source: Acronis
5. Veritas NetBackup for Azure

Veritas provides a scalable backup and recovery solution for Azure that includes integrated security and compliance tools. It supports broad workload coverage and threat detection features.
Note: In late 2024, Veritas was acquired by Cohesity. As of the time of this writing, Veritas NetBackup is still offered as a standalone product.
Key features include:
- Azure workload protection: Covers IaaS and PaaS workloads, including Microsoft 365 and integrated tools.
- Immutable and air-gapped backups: Protects data using isolated and tamper-proof storage.
- AI-driven cyber resilience: Uses analytics and AI to detect threats and support clean data recovery.
- Integrated incident detection and reporting: Connects with Microsoft Sentinel to monitor threats and anomalies.
- Unified compliance and data governance: Manages policies, access, and retention across hybrid environments.
Limitations of Veritas (as reported by users on G2):
- Steep learning curve: The platform offers extensive features, but users often find it challenging to navigate and require training to use it effectively.
- High resource consumption: Backup operations can be resource-intensive, leading to performance impacts on the protected systems.
- Complex upgrade processes: Software upgrades and patching require careful planning and downtime, adding complexity to system maintenance.
- Limited integration with non-Microsoft platforms: While strong in Azure and Microsoft ecosystems, users found Veritas less effective when managing workloads across mixed environments.
- Inconsistent support quality: Support experiences vary, with some users reporting helpful interactions and others citing difficulties in resolving technical issues.

Source: Veritas
First-Party Azure Backup Services
The following are Azure Backup solutions offered as part of the Azure services ecosystem.
6. Azure Backup
Azure Backup is a cloud-native backup solution designed to simplify data protection for Azure resources and on-premises infrastructure. It provides centralized management through the Azure portal and supports automated backups, point-in-time restore, and long-term retention. Azure Backup eliminates the need for on-premises backup infrastructure by offering a pay-as-you-go model that scales with organizational needs.
Key features include:
- One-click backup for Azure virtual machines and workloads
- Application-consistent backups for SQL Server, SAP HANA, and more
- Integrated backup scheduling and retention policy management
- Recovery Services vault for managing backup assets
- Encryption at rest and in transit with Azure Key Vault support
- No maintenance of backup servers or storage infrastructure
Limitations of Azure Backup (as reported by users on G2):
- Limited cross-region backup support: Users noted that Azure Backup lacks flexibility for backing up data across different geographic regions, impacting resilience strategies.
- Slow restore times: Restoring data, especially large datasets, can be slow and impact recovery time objectives (RTO).
- Complex retention policy management: While policy-based, setting up and managing retention rules can be unintuitive for new users.
- Limited application awareness: Some users reported challenges with application-aware backups for non-Microsoft workloads.
- Unclear pricing structure: Cost estimations for long-term retention and storage tiers are not always transparent, making budget forecasting difficult.

Source: Microsoft
7. Azure Site Recovery
Azure Site Recovery enables disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) by replicating workloads running on physical and virtual machines to Azure. In case of an outage, it allows failover to Azure, ensuring business continuity with minimal downtime. Once the primary site is restored, workloads can fail back to on-premises environments with ease.
Key features include:
- Continuous replication of on-premises VMs, Azure VMs, and applications
- Automated failover and failback processes
- Support for recovery plans with scripting and sequencing
- Integration with Azure Monitor for health monitoring and alerts
- Built-in compliance with industry-standard DR requirements
- Cost-efficient DR strategy without secondary datacenter needs
Limitations of Azure Site Recovery (as reported by users on G2):
- Challenging setup for complex environments: Initial configuration, especially for large or hybrid environments, can be complex and time-consuming.
- Limited support for non-Windows platforms: While effective for Windows-based systems, support for Linux or other platforms is less mature.
- Recovery plan rigidity: Customizing recovery plans can be restrictive and may not support all required scripting or sequencing needs.
- Latency during replication: Some users experienced delays or inconsistencies during replication, affecting the reliability of recovery.
- Lack of visibility into replication health: Monitoring tools do not always provide real-time or actionable insights into replication status or health.

Source: Microsoft
8. Azure Archive Storage
Azure Archive Storage is designed for long-term data retention and archival at a low cost. Suitable for storing data that is infrequently accessed but must be preserved for compliance or business needs, it complements active backup solutions by providing a lower-cost storage tier.
Key features include:
- Extremely low storage costs for cold data
- Integration with Azure Backup and lifecycle management policies
- Support for large-scale archival of logs, backups, and compliance data
- Data retrieval options including standard and expedited access
- Secure with encryption and role-based access controls
- Compatible with compliance frameworks such as HIPAA and SEC 17a-4
Limitations of Azure Archive Storage (as reported by users on G2):
- Slow retrieval times: Data retrieval from archive storage can take several hours, which is unsuitable for urgent recovery needs.
- Limited lifecycle management options: Users found policy configurations for data movement and retention somewhat limited and hard to customize.
- Data access complexity: Retrieving data from archive storage requires navigating multiple steps, making it less accessible for non-technical users
- Cost estimation difficulty: Forecasting total costs, including retrieval and early deletion charges, is not straightforward.
- Lack of native search functionality: Users reported that there is no built-in way to search or preview files in archive, complicating data identification.

Source: Microsoft
Conclusion
Azure Backup Services offer a range of options for organizations operating in both cloud-native and hybrid environments. These solutions emphasize automation, security, scalability, and integration to ensure resilient and compliant data protection strategies. However, users should carefully evaluate deployment complexity, support quality, and recovery performance when selecting a backup strategy to ensure alignment with business continuity and regulatory requirements.
What’s next? Consider cross-cloud air-gapping for impenetrable protection.
👉 Download our Multi-Cloud Survival Guide or Multi-Cloud Essentials Checklist