What Is an Azure Backup Policy?
Azure backup policies define how and when backups are created and retained for various Azure workloads. They control the frequency, retention periods, and other aspects of backup management, allowing for tailored data protection strategies. These policies dictate the schedule for creating backups, the duration they are stored, and the recovery point collection settings.
Administrators can create custom backup policies based on organizational requirements, or use Azure’s built-in templates. Once assigned to resources, the policy-driven approach enforces consistent data protection, reducing the risk of human error and simplifying disaster recovery processes.
There are several important aspects to understand when working with Azure backup policies:
- Schedule: Backup policies define the frequency of backups, allowing for options like daily, weekly, monthly, or even more frequent backups (e.g., every 4 hours for VMs).
- Retention: Policies specify how long backups are retained, with options for daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly backups. For example, daily backups might be retained for 30 days, while weekly backups could be retained for 12 weeks.
- Recovery Point Collection (RPC): In the case of Enhanced policies for VMs, RPCs manage snapshots for instant recovery, allowing for quick data restoration.
- On-demand backups: Users can create backups on demand in addition to scheduled backups, allowing for more flexibility.
- Immutable vaults: Azure Backup supports immutable vaults, ensuring that recovery points cannot be deleted prematurely, protecting backups against ransomware and other malicious actors.
- Azure Policy integration: Azure Policy can be used to enforce organizational standards and assess compliance, including enforcing backup policies for VMs and other resources.
Azure backup policies provide the following benefits for organizations:
- Data protection: Ensures data is backed up regularly and retained for the necessary duration, protecting against data loss due to hardware failures, accidental deletions, or disasters.
- Compliance: Enables compliance with industry regulations and organizational requirements.
- Cost optimization: Allows for optimizing backup storage costs by setting appropriate retention periods and moving older backups to less expensive storage tiers.
- Automation: Automates the backup process, reducing manual effort and improving consistency.
In this article:
- Benefits of Using Azure Backup Policies
- Key Aspects of Azure Backup Policies
- Azure Backup Built-In Policy Examples
- Tutorial: Backup an Azure VM Using Enhanced Policy
- Azure Backup Policy Best Practices
Benefits of Using Azure Backup Policies
Azure backup policies offer a structured and automated way to manage backups across Azure resources. Here’s an overview of the key benefits.
Data Protection
Azure backup policies ensure workloads are backed up on consistent schedules, minimizing risks from deletions, hardware failures, or ransomware. Granular recovery points support point-in-time restores, and features like instant restore for VMs enable rapid recovery. Immutable vaults prevent tampering or premature deletion of recovery points.
Compliance
Backup policies enforce retention rules to meet regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. Long-term retention of monthly and yearly recovery points supports multi-year data preservation. Azure Policy integration enables monitoring and enforcement of backup configurations across resources for audit readiness.
Cost Optimization
Retention settings can be customized to balance protection and cost, with short-term backups kept in standard storage and long-term backups moved to archive tiers. Administrators can exclude nonessential disks and adjust schedules for less critical workloads to reduce storage and operational costs.
Related content: read our guide to Azure Backup Pricing
Automation
Backup schedules and retention rules are applied automatically to resources, reducing manual intervention and errors. Policies can onboard new VMs based on tags or resource groups, and Azure Policy ensures ongoing compliance, simplifying backup management at scale.
Key Aspects of Azure Backup Policies
Schedule
In Azure Backup, the schedule defines how often recovery points are created. For Azure virtual machines (VMs), standard policies support daily and weekly backup schedules, while Enhanced policies allow for multiple daily backups—up to every 4 hours.
For workloads like SQL Server or SAP HANA running on Azure VMs, backups can be scheduled as frequently as every 15 minutes using the Azure Backup extension. File shares support daily or weekly backup schedules, and admins can specify the exact time of day for each job, with timezone awareness to align with workload requirements.
A backup schedule determines the frequency and timing of backup jobs. Schedules can be set to trigger backups daily, weekly, or multiple times per day to meet recovery point objectives (RPO).
Retention
Retention rules in Azure Backup policies determine how long each recovery point is kept. Policies support retention for daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly backups, allowing organizations to meet short- and long-term retention requirements.
For example, admins can configure a policy to retain daily backups for 30 days, weekly backups for 12 weeks, monthly backups for 60 months, and yearly backups for 10 years. Retention can also leverage tiered storage: older recovery points may be moved automatically from the Recovery Services vault to the Azure Archive tier for cost savings.
Recovery Point Collection (RPC)
With Enhanced backup policies for Azure VMs, Recovery Point Collection (RPC) enables snapshot-based backups with crash consistency. RPC allows Azure Backup to take multiple recovery points throughout the day without running a full VM backup every time.
These snapshots are stored in the same storage account as the VM, providing relatively rapid recovery capability while Azure Backup manages their lifecycle. Older snapshots are consolidated into less frequent full recovery points as per the policy settings.
On-Demand Backups
In addition to scheduled backups, Azure Backup supports ad-hoc, on-demand backups. Administrators can trigger these backups from the Azure portal, PowerShell, Azure CLI, or REST API.
On-demand backups require specifying a retention duration (e.g., retain for 7 days or retain until a specific date) to avoid cluttering the vault with unnecessary recovery points. This is useful for scenarios like pre-patch snapshots or before major application upgrades.
Immutable Vaults
Azure Backup supports enabling immutability on Recovery Services vaults. When immutability is turned on, recovery points are protected from any deletion, including accidental or malicious deletions by users with vault access. Immutable vaults enforce write-once, read-many (WORM) semantics and support retention lock to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Even administrators cannot override immutability once configured.
Azure Policy Integration
Azure Policy can enforce the presence and configuration of backup policies across subscriptions and resource groups. For example, an organization can deploy a policy that ensures all Azure VMs in a specific scope are backed up to a Recovery Services vault with a defined policy.
Built-in policy definitions such as “Audit virtual machines without disaster recovery configured” help identify non-compliant resources. Admins can combine Azure Policy with automated assignment of backup policies when new VMs are provisioned.
Azure Backup Built-In Policy Examples
Azure provides a set of built-in backup policies that simplify the deployment and enforcement of standardized data protection practices across environments. These policies help organizations manage backups based on resource tags, vault configurations, and security requirements. Below are some key examples:
1. Configure VM Backups to a New Recovery Services Vault
This policy targets virtual machines (VMs) with specific tags and automatically backs them up to a newly created Recovery Services vault located in the same resource group. It’s suitable for distributed teams where each group is responsible for its own resource protection.
2. Configure VM Backups to an Existing Vault
This policy enforces backup of all tagged VMs to an existing vault within the same region. It supports centralized management, allowing a shared operations team to maintain consistent backup practices across a subscription.
3. Configure Tagless VM Backups to a New Vault
For VMs without any tags, this policy deploys a new vault in the same resource group and location as the VM. It gives individual application teams control over the backup configuration without relying on a tagging strategy.
4. Configure Tagless VM Backups to an Existing Vault
This policy routes untagged VMs to an existing central vault, enabling a subscription-wide backup strategy. It is particularly useful when a centralized operations team is responsible for ensuring all VMs are protected, regardless of tagging.
5. Use Customer-Managed Keys to Encrypt Backup Data
By default, Azure uses service-managed keys for encryption. This policy enables the use of customer-managed keys stored in Azure Key Vault. It provides greater control over encryption and helps meet compliance requirements that mandate user-controlled cryptographic keys.
6. Use Azure Private Link for Backup Services
This policy enables secure, private connectivity between the network and Azure Backup services, eliminating the need for public IP addresses. By using Azure Private Link, data transfer paths are restricted to the Microsoft backbone network.
7. Configure Private Endpoints for Backup Vaults
Similar to Private Link, this policy configures private endpoints for Recovery Services vaults. It ensures that access to backup data is restricted to authorized private network interfaces.
- Use Lifecycle Policies to Save Money: Set up lifecycle policies to move old backups to cheaper storage options like Amazon S3 Glacier. This can help you save a lot of money on storage costs.
- Back Up to Different Regions and Accounts: Make your disaster recovery plan stronger by copying backups to different AWS regions or accounts. This protects your data from region-specific problems and security issues.
- Automate Your Backup to Reduce RTO: Use AWS Backup to set up frequent backup intervals. Automating backups every hour or even every few minutes ensures you can recover data quickly, minimizing downtime.
- Tag Your Resources for Easy Management: Tags help you quickly identify and group related backups, making it easier to manage them and to monitor costs. This can also simplify reporting and compliance checks.
- Test Your Disaster Recovery Plan Regularly: Automate DR drills to check your backup and recovery processes. Make sure your backups work and that you can restore data quickly to find and fix any potential problems.
Tutorial: Backup an Azure VM Using Enhanced Policy
To back up an Azure virtual machine using the Enhanced policy, follow the steps below in the Azure portal. Enhanced policies offer features such as higher backup frequency, zonal resiliency, and longer snapshot retention in the operational tier.
- Select a recovery services vault
Open the Azure portal and choose a Recovery Services vault that will manage the VM backup. - Navigate to backup policies
In the selected vault, go to the Backup section and select Backup Policies. Click on +Add to create a new policy.
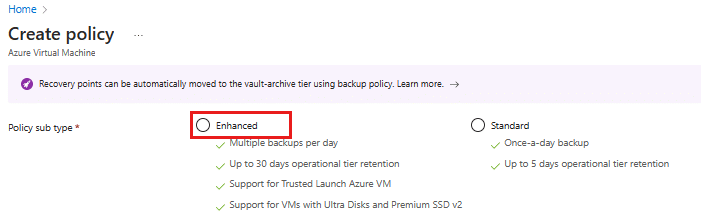
- Choose the policy type
When prompted to select a policy type, choose Azure Virtual Machine. Then, under Policy sub-type, select Enhanced to enable the new policy capabilities.
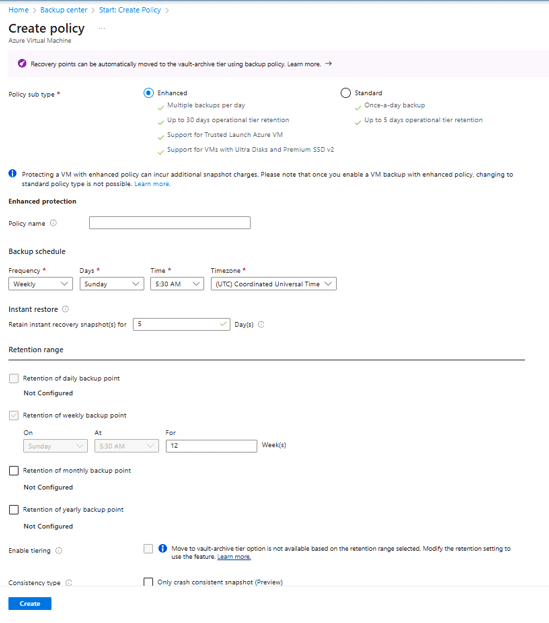
- Configure backup schedule
Users can configure the schedule to back up the VM hourly, daily, or weekly. Hourly schedules allow a minimum recovery point objective (RPO) of 4 hours, with available intervals of 4, 6, 8, 12, or 24 hours. For example, a policy set to back up every 4 hours over a 24-hour period results in 6 snapshots per day. - Set instant restore retention
Choose how long to retain snapshots in the operational tier. This can range from 1 to 30 days. The default is 7 days. Note that the number of snapshots per day affects the allowed retention period—more frequent snapshots reduce the maximum retention window. - Customize retention settings
The policy auto-populates default retention for daily (180 days), weekly (12 weeks), monthly (60 months), and yearly (10 years) backup points. Users can adjust these settings as needed. - Finalize and create the policy
Review the configuration and click Create to deploy the Enhanced policy. Once created, assign the policy to the VM to begin scheduled backups.
Source: Microsoft
Additional capabilities
- Enhanced policy supports trusted launch VMs, Premium SSD v2, Ultra SSD, and zonal redundancy through Zone-redundant storage (ZRS).
- Selective disk backup and restore is supported. Users can exclude noncritical data disks to reduce backup costs and restore times.
- VMs with public network access disabled are also supported for backup.
- Migration from standard to enhanced policy is available in preview, allowing existing protected VMs to benefit from these features.
Azure Backup Policy Best Practices
Here are some of the ways that organizations can ensure the most effective use of Azure backup policies.
1. Schedule Considerations
When designing backup schedules, it’s important to align the backup frequency with the criticality of the workload. For mission-critical resources, configure the highest available backup frequency to reduce recovery point objectives (RPO). For example, enhanced policies support backups every 4 hours.
To reduce the impact on production workloads, schedule backups during non-peak hours—such as between 2–3 AM. Additionally, to avoid network congestion and performance issues when backing up many virtual machines, stagger backup jobs by creating separate policies. For example, if backing up 500 VMs, consider creating five policies, each assigned to 100 VMs and spaced a few hours apart.
Grouping resources that share the same backup schedule, start time, and retention configuration under a single policy helps maintain consistency and reduces configuration complexity.
2. Retention Considerations
Backup retention falls into two categories: short-term (daily backups) and long-term (weekly, monthly, yearly backups). Use long-term retention when you know in advance that data needs to be stored for extended periods due to compliance or regulatory mandates. Azure Backup supports storing long-term recovery points in the archive tier to optimize storage costs.
On-demand backups can have their own custom retention settings, independent of the policy. This is useful when backups are needed outside the regular schedule, such as before applying critical updates. Note that retention rules defined in the policy do not apply to these ad hoc backups.
3. Optimize Backup Policy
Backup policies should be revisited periodically to align with evolving business requirements. If you increase retention duration, existing recovery points are preserved under the new rule. If you reduce it, older recovery points are marked for deletion in the next cleanup cycle.
When decommissioning resources, consider stopping protection while retaining backup data. This retains existing recovery points for future restore operations. Alternatively, stopping protection and deleting backup data removes all recovery points and disables restores.
Remember that a policy is scoped to a specific vault, and each policy has a limit on the number of items (e.g., 100 VMs). Use multiple policies to scale protection. Note that scheduled backups cannot be entirely disabled; the minimum supported schedule is one backup per week.
4. Security Considerations
Security in Azure Backup includes identity management, encryption, and protection from accidental or malicious deletion.
Use Azure role-based access control (RBAC) to enforce least-privilege access. Assign built-in roles like Backup Contributor, Operator, and Reader to segregate duties and limit permissions based on user responsibilities. For example, monitoring personnel should not have permissions to modify or delete backup data.
Backup data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. Azure uses Microsoft-managed keys by default but supports customer-managed keys for organizations with stricter encryption requirements.
Soft-delete is enabled by default and retains deleted backup data for 14 additional days at no cost, offering protection against accidental or malicious deletion. To prevent tampering with this feature, enable multi-user authorization (MUA), which requires approval from a security administrator before critical operations like disabling soft-delete can proceed.
5. Governance Considerations
Governance can be enforced using Azure Policy to ensure backup coverage and compliance at scale. Admins can automatically enable backups for new virtual machines based on resource tags or groupings, ensuring that no resource is left unprotected.
Use built-in policies to auto-enable backups based on organizational ownership models—either centrally managed or delegated to application teams. For compliance tracking, implement audit-only policies that detect resources without backup configured.
Monitoring policies can also configure diagnostic settings for all vaults to send logs to Log Analytics, supporting large-scale visibility and compliance tracking. These governance tools ensure consistent protection and help meet regulatory and operational standards across the Azure environment.
Automating Azure Backup with N2W
Azure Backup Policies help enforce retention rules—but N2W takes it a step further with cross-cloud automation, cost optimization, and faster recovery from a single console.
- Automated Lifecycle Policies: Archive backup data to Azure Blob, AWS S3, or Wasabi with per-VM retention rules—no scripts needed.
- Unified Management: Manage backups across Azure, AWS, and Wasabi in one dashboard—no toggling or duplication.
- Faster Recovery: Restore entire VMs or specific files in seconds, with multi-generation restore points and agentless SQL backup.
- Cross-Cloud DR: Copy backups between regions and platforms for air-gapped protection—ideal for compliance or ransomware resilience.
- Major reduction in long-term backup costs (over 80%): by eliminating high and unpredictable licensing fees and using cheaper, tiered Azure Blob storage for backups
Want smarter backup policies—without more manual work?
🎯 Start your free 30-day trial and automate your Azure backup lifecycle with N2W.