What Are Azure Backup Solutions?
Azure backup solutions protect data stored on Microsoft Azure platforms, or use Azure cloud resources to backup data stored elsewhere. These solutions help organizations secure their critical workloads, databases, and applications in the cloud. By using these tools, organizations can manage backup processes, automate disaster recovery, and reduce downtime in case of data loss or system failures.
Azure backup solutions typically support features like incremental backups, encryption, and easy restore capabilities, ensuring compliance while maintaining high uptime. Advanced solutions offer features like hybrid backup strategies, cross-region backup storage, and AI-enhanced insights into backup health.
In this article:
- The Need for Azure Backup Solutions
- Notable Azure Backup Solutions
- How to Choose the Right Azure Backup Solution
The Need for Azure Backup Solutions
As organizations increasingly migrate workloads to the cloud, the need for backup and disaster recovery becomes critical. While cloud platforms like Azure offer inherent resilience, they don’t replace the need for dedicated backup solutions. Data can still be lost due to human error, malicious attacks such as ransomware, or accidental deletions. Without a reliable backup system in place, recovering this data can be costly or even impossible.
Compliance and regulatory requirements further underscore the importance of having a well-defined backup strategy. Many industries must adhere to strict data retention and recovery policies. Azure backup solutions help meet these mandates by offering secure, policy-driven backup configurations that ensure data is retained and recoverable over required periods.
Notable Azure Backup Solutions
1. N2WS
N2W is the leading cloud-native backup and disaster recovery platform built for AWS and Azure public clouds. N2W pioneered cloud-native data protection on AWS and has spearheaded into Microsoft Azure bringing its revolutionary data protection capabilities to enterprises in an effort to eliminate complex backup management and deliver peace of mind knowing IT teams can recover both full environments and single files in a matter of minutes. N2W is a tool that sits on top of the users’ cloud(s) using policy-driven backup operations under a single console. Teams enjoy immediate recovery from any region, subscription, even across clouds. It also has extremely cost-effective, secure data lifecycle management into Azure Blob storage.
Key features include:
- Multi-Cloud Backup Support – N2W provides centralized backup and recovery across AWS and Azure, allowing unified management and visibility of cloud data protection operations in hybrid or multi-cloud environments.
- Azure Resource Flexible Backup – Supports automated, snapshot-based backups for Azure virtual machines using native Azure APIs, enabling fast and application-consistent backups that can be taken as little as every five minutes, with minimal performance impact.
- Easy-To-Use Policy-Driven Automation – Enables scheduling and retention policies for Azure resources (and AWS) under a single console without the need to toggle back and forth. N2W automates backups, lifecycle management, and archives to optimize costs and maintain compliance.
- Instant Recovery & Cross-Region and Cross-Subscription Restore – Delivers near-instant recovery of Azure VMs and the ability to restore across regions and subscriptions, supporting disaster recovery and geographic redundancy.
- Cost Optimization & Storage Tiering – Allows tiering of incremental backup data to Azure Blob Storage for long-term retention and cost-effective storage management potentially saving up to 92%. Pricing is completely transparent and based on number of VMs, rather than complicated tiering based on size.
- Secure & Compliant Storage – Backups are encrypted both in-transit and at-rest, and users can leverage RBAC and IAM policies for secure access controls, aligned with compliance standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Monitoring & Reporting – Built-in reporting and alerting tools offer visibility into backup health, SLA compliance, and usage metrics across Azure and AWS resources.
- Regular, Automated DR Testing – Supports non-disruptive DR testing by allowing users to spin up isolated copies of Azure VMs from backups in alternate regions or subscriptions. Users can schedule drills regularly, prioritize resources and prepare for worst-case scenario with full-healthy failover checks, network settings recovery and comprehensive reporting (great for compliance teams).
Advantages of N2W for Azure Users:
- Unified AWS + Azure Protection: Ideal for organizations running workloads across both clouds, consolidating backup management under one pane of glass.
- Faster Recovery Times: Snapshot-based backups allow near-zero RTOs for Azure VMs.
- Cost Efficiency: Native snapshot usage and tiering to low-cost storage help reduce backup and retention costs. In addition, N2W charges a flat rate regardless of VM size.
- Minimal Infrastructure Overhead: Operates as a lightweight solution with minimal impact on performance or additional Azure resources.
- Scalable for Enterprise: Supports large-scale environments and is frequently used by managed service providers and enterprises with compliance and governance needs.
2. Cohesity
Cohesity is an enterprise data protection platform that helps organizations protect Azure-based resources—like Azure VMs, Azure SQL, Microsoft 365, and Azure Stack Hub—against threats such as ransomware and accidental data loss.
Key features include:
- Centralized management: Unified platform for managing backups across Azure, SaaS, and on-prem environments using a global UI.
- Hybrid cloud support: Protects both Azure-native and hybrid workloads, including Microsoft 365 and Azure Stack Hub.
- Ransomware protection: Multilayered security with data isolation features like virtual air-gapped storage (FortKnox) to protect against cyber threats.
- Data services: Offers backup, disaster recovery, test/dev, archiving, and cyber vaulting within a single solution.
- Long-term retention: Supports durable, policy-based data retention strategies for compliance and recovery needs.
Limitations of Cohesity:
- Reporting limitations: Many users have noted that the reporting capabilities are basic and lack customization options. Reports often do not provide granular insights or detailed metrics about data protection activities, which limits their usefulness for large enterprise environments. Additionally, generating advanced reports often requires support tickets or leveraging APIs, which may not be ideal for all users.
- Inefficient restore process: Several users have experienced delays during file-level restores, with even small files taking hours to recover. This inefficiency could lead to operational disruptions, especially during critical recovery scenarios. Some users have also reported challenges with restoring SQL databases or instances due to the lack of batch recovery options.
- Cost and licensing concerns: Some users believe the pricing could be more competitive. Certain features, such as advanced cyber resilience tools, are limited or require additional costs, reducing affordability for smaller organizations.
- Interface and usability issues: The user interface, while functional, is not as intuitive or user-friendly as competitors’ platforms. Navigation can feel clunky, and certain tasks require additional steps or workarounds. Users also mentioned that search functionality, such as locating backups, could be more precise and efficient.
- Support for legacy systems: Organizations with older systems have reported difficulties with legacy hardware and software support. For example, Cohesity lacks comprehensive compatibility for older operating systems and backup platforms like Windows 2003 or legacy Oracle workloads, which some competitors still support.
- Delays in feature rollouts: Users have expressed frustration with the pace of feature releases. For example, capabilities such as advanced AI-based analytics, enhanced reporting, and simplified cloud migration tools are often delayed. Additionally, while some features exist, they may not be as robust as expected, requiring frequent updates or fixes.
Source: Cohesity
3. Veeam

Veeam is a backup and recovery solution providing enterprise data protection for Microsoft Azure environments. It provides automated, policy-based backups, full and file-level restores, and security features like immutability and role-based access.
Key features include:
- Automated protection: Enables policy-driven backup processes that auto-discover and secure Azure workloads.
- Immutable storage: Uses Azure Blob’s WORM capabilities to protect backups from tampering and ransomware.
- Granular recovery: Supports both full instance and file-level recovery within Azure or across regions and subscriptions.
- Layered security: Includes logically air-gapped backups, least-privilege IAM, and RBAC for strong access control.
- Hybrid and multi-cloud ready: Offers consistent operations across Azure, on-premises, and other cloud platforms when paired with Veeam Backup & Replication.
Limitations of Veeam:
- Limited deployment flexibility: Veeam’s reliance on CloudFormation templates for AWS limits users who prefer custom naming schemes or manual deployments.
- Challenging backup configuration: Creating backup policies often involves extensive tagging and lacks intuitive guidance, posing difficulties for teams unfamiliar with infrastructure internals.
- Lack of multi-tenancy: The solution does not support multi-tenancy, limiting its use for MSPs who need to provide separate backup consoles for individual clients.
- Outdated terminology: Veeam uses on-premise terminology for cloud solutions, such as referring to backups as “replicas,” which can confuse users accustomed to modern cloud terminology.
- Recovery limitations: The recovery process is cumbersome, requiring users to know specific resources for restoration, as policies are not searchable or linked to the recovery workflow.
- Security exposure with file-level restore: Restoring files directly to production instances could pose risks—especially if malware is present in the backup set.
- Immutability gaps: Veeam does not support immutable EBS snapshots for AWS but does offer S3 object lock for certain storage classes. However, it lacks support for cost-efficient options like S3 Infrequent Access.
- Ineffective cost estimation: The cost estimation tool for archives often provides inaccurate calculations due to its inability to account for all variables, reducing its utility for budget planning.
- Inefficient cleanup: Unused backups can only be cleaned up once daily, potentially leading to unnecessary Azure storage costs until the next cleanup cycle.
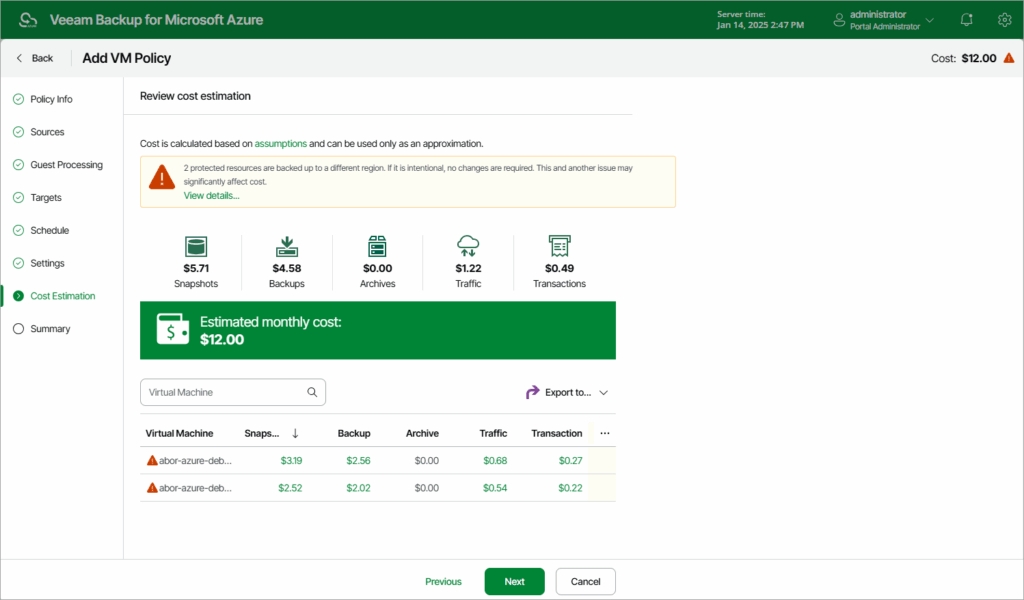
Source: Veeam
4. Rubrik
Rubrik provides cloud-native backup and cyber recovery solutions for Microsoft Azure, helping organizations secure data across VMs, databases, and SaaS services. It delivers ransomware protection, data immutability, automated recovery, and long-term retention\.
Key features include:
- Azure coverage: Supports Azure VMs and Managed Disks, Azure SQL, Microsoft 365, Azure VMware Solution, Azure Files, and Azure NetApp Files.
- Immutable snapshots: Creates immutable backups, logically air-gapped and resistant to ransomware, with encryption in-flight and at rest.
- Automated protection: Auto-discovers resources and applies backup policies by tags, resource groups, or subscriptions.
- Flexible recovery: Allows crash-consistent restores, file-level recovery, or VM recreation in the same or different Azure subscriptions.
- Cloud-native design: Uses native Azure snapshot APIs without requiring persistent infrastructure in the cloud or on-prem.
Limitations of Rubrik (as reported by users on G2):
- Slow and inconsistent restores: Several users report delays in performing file-level and full VM restores, particularly in larger environments. Recovery times are not always predictable, and performance varies depending on resource size and storage configuration.
- User interface complexity: The interface is often described as unintuitive, with a steep learning curve for new users. Navigating backup policies and recovery workflows can require multiple steps and lacks clear guidance in some areas.
- Search and reporting gaps: Users have noted that search functionality within the console is limited, making it difficult to locate specific snapshots or backup jobs quickly. Reporting features are basic and lack advanced customization.
- Policy management challenges: Applying or modifying backup policies at scale can be time-consuming. Tag-based automation is helpful, but users mention that initial setup is not straightforward and often requires consulting support or documentation.
- Integration and compatibility issues: While Rubrik supports a range of workloads, users point out that integration with certain Azure-native services or APIs is still evolving. This can limit the solution’s effectiveness in fully cloud-native environments.
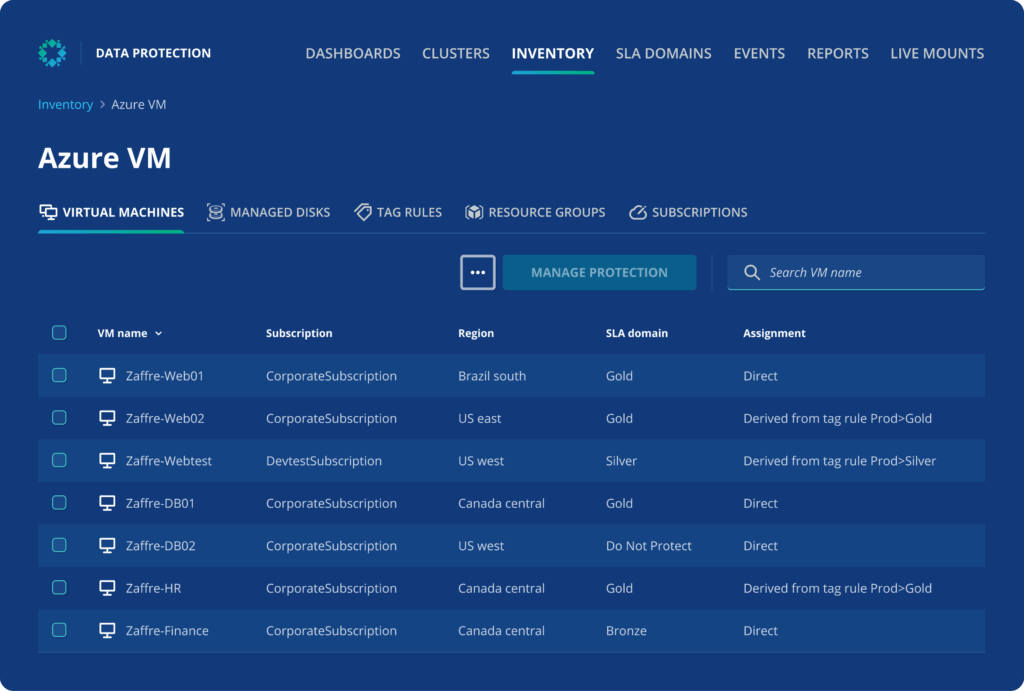
Source: Rubrik
5. Druva

Druva offers an agentless, cloud-native backup solution for Microsoft Azure VMs. It aims to deliver secure, scalable, and cost-efficient data protection without requiring complex infrastructure or incurring egress fees.
Key features include:
- Agentless backup: Protects Azure VMs without installing agents or managing additional infrastructure, reducing deployment complexity.
- Air-gapped, encrypted storage: Stores backup copies in Druva’s secure cloud, isolated from attackers and encrypted in transit and at rest.
- No egress fees: Eliminates hidden cloud costs by avoiding Azure egress fees during data recovery.
- File-level restore: Enables flexible recovery options including full VM restoration or selective file/folder-level recovery.
- Global deduplication: Reduces backup storage footprint and costs by eliminating duplicate data across workloads.
Limitations of Druva:
- Dependency on SaaS infrastructure: As a fully SaaS-based solution, Druva relies entirely on its cloud-hosted interface. If this interface experiences downtime, users are unable to manage or recover backups until the issue is resolved, with no control over resolution timelines.
- Limited AWS region support: Druva supports only 14 AWS regions and GovCloud, restricting flexibility compared to solutions with broader global region support.
- Rigid scheduling options: Backup policies in Druva are limited to daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly schedules, lacking the granularity offered by competitors that support minute-level scheduling.
- No cross-cloud support: Druva does not provide functionality for cross-cloud backup or recovery, limiting versatility for multi-cloud strategies.
- Learning curve: Some users find Druva less intuitive compared to alternatives, which offer simpler and more user-friendly interfaces.
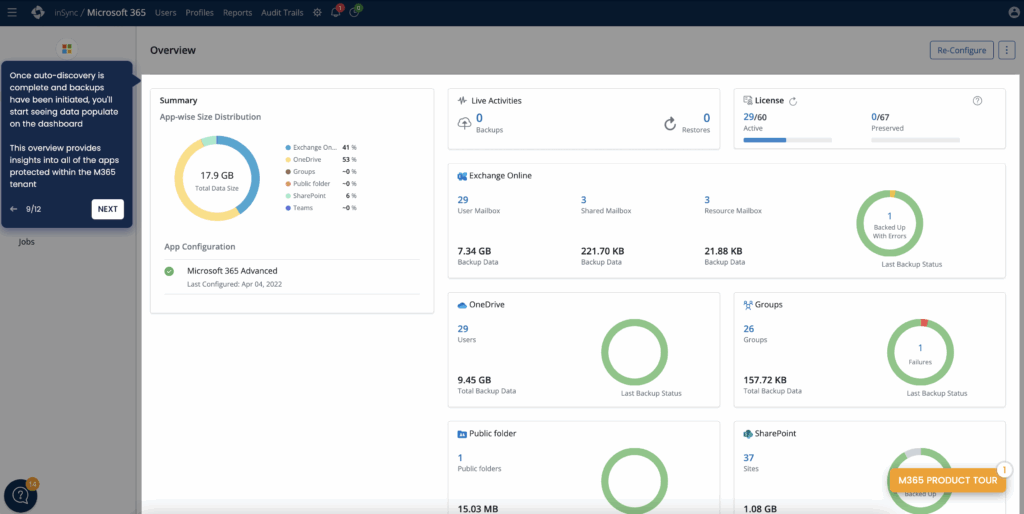
Source: Druva
6. Commvault

Commvault offers enterprise data protection for Microsoft Azure through its Commvault Cloud platform, with backup, recovery, and cyber resilience capabilities. Powered by Metallic AI, it enables organizations to protect Azure workloads and hybrid environments using a SaaS model.
Key features include:
- Workload coverage: Protects a range of Azure and hybrid workloads across virtual machines, databases, SaaS, and on-premises systems.
- SaaS delivery model: Delivers backup and recovery as a service with no hardware, maintenance, or upfront infrastructure investment.
- Ransomware defense: Employs threat detection and response tools to detect, isolate, and recover from ransomware attacks.
- Immutable backups: Ensures data is tamper-proof with built-in immutability, logical air gaps, and zero-trust access controls.
- Granular recovery: Offers flexible restore options, including file-level recovery and targeted data restoration.
Limitations of Commvault:
- Access management concerns: As a SaaS solution, Commvault’s reliance on cloud-hosted services raises potential privacy and access management challenges for organizations handling sensitive data.
- Limited snapshot archiving: Commvault cannot archive RDS snapshots to cold storage solutions like S3 or Azure Blob, which limits cost-effective long-term storage options.
- Complex cross-cloud recovery setup: While cross-cloud recovery is supported, it requires a virtual server acting as an HTTP/HTTPS proxy, introducing additional costs and a potential single point of failure.
- Restricted DR backup flexibility: Disaster recovery backups must be stored in object storage (e.g., S3 or Azure Blob), which can lead to longer recovery times compared to snapshot-based DR backups.
- Challenging infrastructure optimization: Architecting and scaling deduplication servers and optimizing backup jobs require expertise, making the platform less accessible for teams without dedicated specialists.
- Policy limitations: Users cannot include multiple resource types in a single Azure backup policy, which may complicate backup management for diverse workloads.
- Incomplete VPC backup support: Commvault only backs up attributes of EC2 instances within a VPC, not the entire VPC itself, limiting comprehensive recovery options for cloud environments.
- No VPC cloning or recovery scenario features: The platform lacks tools to easily clone VPCs or orchestrate rapid, full-infrastructure recovery, reducing efficiency during large-scale disaster recovery operations.

Source: Commvault
7. MSP360

MSP360 provides a flexible backup solution that integrates with Microsoft Azure to deliver secure and scalable data protection across multiple platforms. Built for managed service providers and IT teams, it offers centralized control, easy deployment, and compatibility with major operating systems and cloud environments.
Key features include:
- Azure integration: Natively supports Microsoft Azure cloud storage, enabling direct backup to Azure with minimal configuration steps.
- Centralized management: Unified web-based console for monitoring, managing, and reporting across protected endpoints and storage accounts.
- Multi-platform support: Backs up data from Windows, Linux, macOS, VMware, Hyper-V, Microsoft 365, and Google Workspace.
- File and system image backup: Supports both file-level and full system image backups.
- Synthetic full backups: Reduces backup time and bandwidth by only uploading changed data blocks to Azure.
Limitations of MSP360 Backup:
- Performance issues: Backup performance in terms of speed has been noted as suboptimal. Users have reported that backups can take longer to complete compared to other solutions, especially for large datasets. This can lead to delays in both backup and recovery operations during critical scenarios.
- Complex update process: The software’s update cycle is not intuitive and has not seen significant improvements over the years, despite feedback from users. This can result in a frustrating experience when upgrading to new versions or applying patches.
- Limited support for critical backups: Some users feel MSP360 Backup is not well-suited for mission-critical backups or full disaster recovery solutions. The lack of local immutable storage backup options is a particular shortcoming for organizations needing ransomware protection or compliance with data integrity standards.
- Rudimentary SharePoint and Office 365 Restore: Microsoft 365 SharePoint restore functionality is basic and can make finding and restoring files or folders from large document libraries cumbersome. This is a limitation for organizations heavily dependent on Office 365 for their workflows.
- Web portal and user interface challenges: The interface has been described as clunky and difficult to navigate, particularly for new users. The web portal login expiration can also be annoying, and some users have expressed a desire for a desktop-based GUI for easier management. Additionally, certain menu items are inconsistently located, requiring users to search unnecessarily.
- Customer support issues: Customer support quality is inconsistent. While some support representatives provide excellent service, others are less responsive, particularly for escalated Tier 2 or Tier 3 issues. Delays in resolving “Priority 1” issues have been reported, which can be critical during downtime.
Source: MSP360
8. Zerto

Zerto, part of HPE, delivers disaster recovery and workload mobility solutions for Microsoft Azure, offering data protection, recovery, and migration across cloud environments. It enables organizations to protect, move, and recover Azure workloads with minimal disruption.
Key features include:
- Continuous data protection (CDP): Achieves recovery point objectives (RPOs) measured in seconds by continuously replicating changes, reducing potential data loss.
- Recovery orchestration: Supports full-site, application, VM, or file-level recovery from any point in time, with recovery time objectives (RTOs) in minutes.
- Scalable, agentless architecture: Deploys without agents and supports thousands of Azure VMs via scalable Azure-native components like scale sets and storage accounts.
- Cloud mobility: Enables easy migrations into, out of, or between Azure regions without impacting production systems or requiring reconfiguration.
- In-cloud disaster recovery: Provides orchestrated failover and protection between Azure regions, using Azure as a disaster recovery target.
Limitations of Zerto (as reported by users on G2):
- High Cost for Smaller Deployments: While Zerto is valued for enterprise-scale recovery, smaller organizations find its pricing model difficult to justify. The cost may outweigh the benefits for environments with modest recovery needs.
- No native backup capabilities: Zerto can handle disaster recovery but lacks full-featured backup functionality, such as long-term retention or file-level backup granularity. Users often need to pair it with a separate backup solution to meet compliance or retention goals.
- Complex setup and configuration: Initial deployment, especially in Azure environments, can be complex. Users mention that setting up virtual replication appliances and configuring network mappings often requires help from Zerto support or professional services.
- Limited automation and customization: Some users express a desire for more flexible automation options. While failover orchestration is strong, scripting and integration for custom workflows or alerting is more limited compared to other platforms.
- UI usability issues: The web interface, while functional, is seen as outdated and occasionally sluggish. Some users report difficulty in navigating between tasks or quickly identifying problem areas during replication or recovery operations.
Source: Zerto
How to Choose the Right Azure Backup Solution
Choosing the right Azure backup solution depends on a mix of technical requirements, compliance needs, and operational preferences. Here are the key factors to evaluate when making your selection:
- Workload support: Verify that the solution can protect all critical assets, including virtual machines, structured databases, file shares, and cloud-native applications. Consider whether it supports hybrid and SaaS environments if the infrastructure spans multiple platforms.
- Deployment architecture: Decide between a SaaS-based solution and one that requires infrastructure deployment. SaaS simplifies operations but may offer limited control. Infrastructure-based deployments allow deeper customization but introduce additional management overhead.
- Recovery capabilities: Evaluate the ability to meet recovery point objectives (RPOs) and recovery time objectives (RTOs). Solutions should offer flexible restore options—full, granular, and cross-region—to match workload sensitivity and downtime tolerance.
- Security and compliance: Look for features like immutability, encryption (in-transit and at-rest), and air-gapped storage. Role-based access controls and native identity integrations improve security, while policy-based retention and audit capabilities support compliance with industry regulations.
- Cost efficiency: Assess licensing models and storage optimization features such as deduplication, compression, and incremental backups. Consider tools that offer cost predictability and eliminate fees related to data recovery or long-term retention.
- Scalability and administration: The solution should support large-scale environments and allow centralized management across regions and resource types. Automated policy enforcement, intuitive interfaces, and robust monitoring reduce operational complexity.
- Integration with Azure services: Ensure tight integration with Azure-native APIs, identity services, and storage layers. Compatibility with tools like Azure Policy and monitoring services ensures smoother operations and fewer performance bottlenecks.
- Disaster recovery support: Beyond backup, evaluate whether the solution offers disaster recovery orchestration, including automated failover, test environments, and region-to-region replication. Effective DR capabilities reduce downtime and simplify compliance testing.
Conclusion
Azure backup solutions aid in protecting cloud-based workloads by ensuring data availability, integrity, and recoverability across diverse IT environments. With growing reliance on cloud infrastructure, these solutions help address the challenges of data loss, compliance, and operational continuity.
If you’re looking at Azure Backup Solutions as part of a cross-cloud or multi-cloud strategy, download our free checklist for the 10 must-have features in a solution.