In today’s modern era, individuals and businesses are increasingly relying on cloud computing platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) to store and manage their data. AWS provides numerous storage services, each with a distinct pricing structure and set of features, so estimating how much your AWS storage costs will be often proves to be challenging.
This article will explore the factors determining AWS storage costs, offer insights into various storage tiers, elaborate on pricing structures, and present actionable strategies to optimize expenditure.
What Factors Determine Your AWS Bill?
Navigating AWS storage costs requires grasping several key components that influence storage pricing.
Charges Based on Storage Usage
AWS bills are based on the amount of data stored within the AWS infrastructure. The fundamental metric here is the gigabyte per month rate, representing the volume of data stored during a billing cycle.
For instance, the gigabyte per month rate for S3 Standard is $0.023 per GB per month in the US East (N. Virginia) region. The gigabyte per month rate for Amazon EBS General Purpose SSD is $0.05 per GB per month in the same region.
Type of Storage
AWS offers different storage services with different features and prices. Amazon S3, for instance, is designed to store large amounts of unstructured data. Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) is block storage built for storing data with high performance.
Amazon S3 offers different levels of storage, each with its own unique pricing and availability. For instance, with S3 Standard, you can frequently access data with instant availability. With the S3 Infrequent Access tier, you can store data at lower prices, but it will take longer to access.
EBS also provides various volume types, each having distinct price and efficiency features. Amazon EBS General Purpose SSD is designed for general-purpose workloads and offers a good balance of performance and cost. Amazon EBS Provisioned IOPS SSD is designed for workloads that require high IOPS and offers the highest performance, but it is also the most expensive volume type.
Access Rates
Different AWS storage tiers have different access patterns that affect their costs. For example, S3 Standard allows you to access data frequently with instant availability, while S3 Infrequent Access gives you less frequent access but offers lower prices.
If you have frequently accessed data, you will want to use a storage tier that offers instant availability. Instant availability will ensure that your data always remains accessible.
If you have data that you don’t need to access as frequently, you can use a storage tier that offers lower prices while compromising the speed at which you can access your data.
With N2W, we automate the process of data transfer to ensure that you are taking advantage of the most cost-efficient storage tier for your availability and latency needs.
Data Egress
Data egress is the cost of transferring data to an external network from your AWS environment. For example, downloading data from an S3 bucket to your computer will incur a cost for data egress.
The rate for data egress varies depending on the region where your data is stored and where you are transferring the data to. The AWS Pricing Calculator is available to estimate your costs, although determining your data egress patterns with just this tool can be challenging. (TIP: to help you navigate the calculator, check out this blog post).
Data Transfer
Data transfer is the cost of transmitting data among AWS services. This means that if you move data from, say, an EC2 instance to an S3 bucket, you will be charged for data transfer.
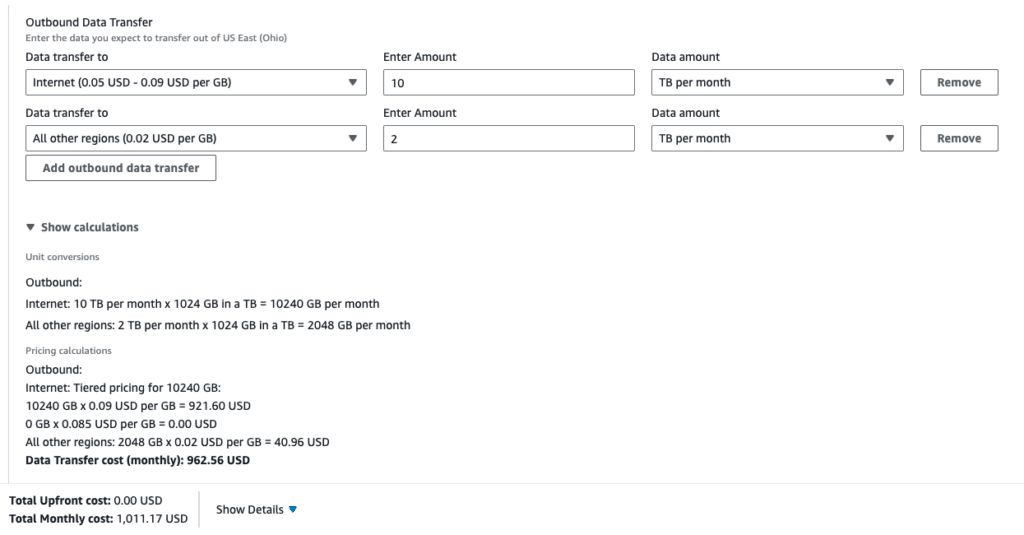
The data transfer rate varies based on the type of storage used and the location of the data. For example, the outbound data transfer rate for Amazon S3 to an internet location is $0.09 per GB in the US East (N. Virginia) region.
Replication
Replication is the process of copying data to multiple locations for redundancy and disaster recovery. Replication can add to your storage costs. The replication price depends on the kind of storage used and the data storage location.
The cost of replicating object data to another region in AWS is typically the same as the cost of storing the data in the first place. Here we have a cross-region example with an S3 source bucket in us-east-2.
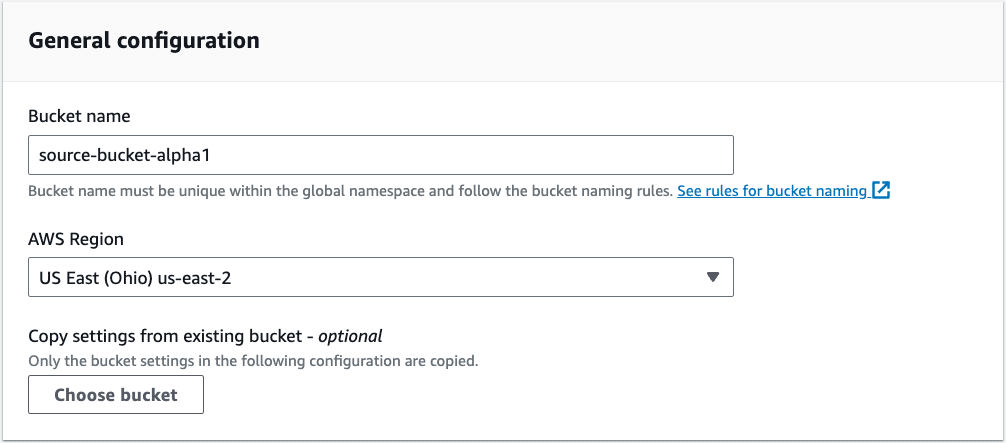
When setting your target replication bucket, you can see the need to enable versioning. This will also incur additional costs that need to be accounted for.
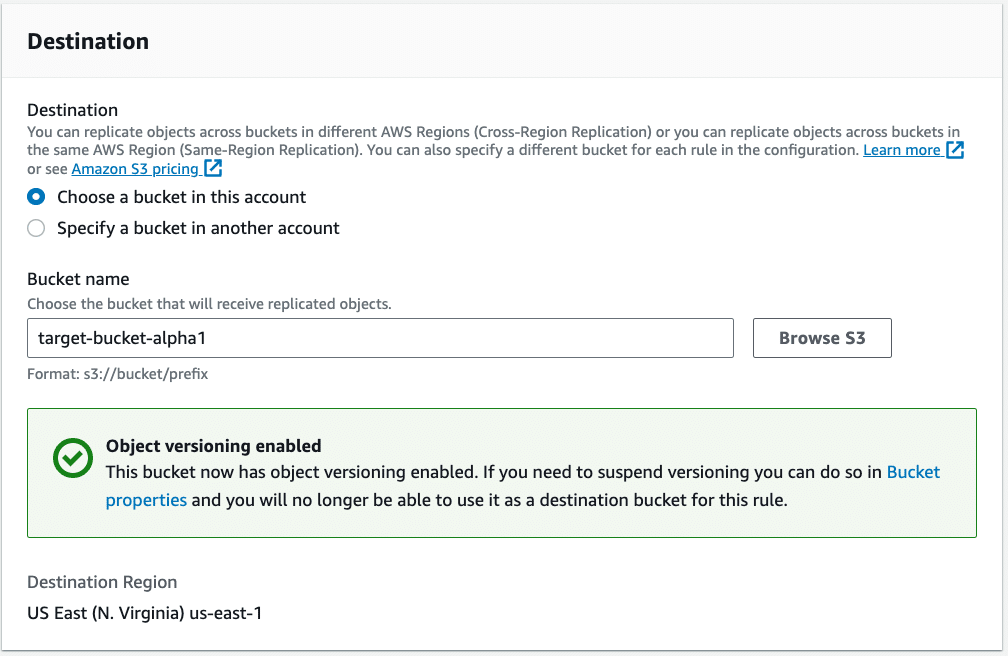
Understanding the configuration options that determine your AWS charges is crucial. Monitoring and managing these charges regularly should be included in operational practices and aligned with your business policies. Just S3 alone will have many configuration options. What about the rest of the storage options in AWS?
Fortify your cloud across every critical dimension.
- Efficiency + Optimization
- Security + Control
- Orchestration + Visibility

Overview of AWS Storage Services
AWS offers a wide variety of storage tiers to meet the diverse needs of its customers. Here is a brief overview of some of the most popular storage tiers:
Elastic Block Store (EBS)
EBS provides storage at the block level for EC2 instances. Each volume type has its own cost and performance characteristics.
- General Purpose SSD: General Purpose SSD is designed for general-purpose workloads and offers a good balance of performance and cost. It is a viable choice for apps, such as web servers and databases, that require consistent performance.
- Provisioned IOPS SSD: Provisioned IOPS SSD is designed for workloads that require high IOPS, such as high-performance databases and real-time analytics. It offers the highest performance of all EBS volume types, but is also the most expensive.
- Cold HDD: Cold HDD is designed for low-cost workloads that can tolerate longer access latency. It is a great option for storing infrequently accessed data, such as backups and archives.
Simple Storage Service (S3)
Amazon S3 is a highly elastic object storage solution that has the ability to store massive amounts of data. S3 itself offers a variety of storage classes, each with its own price and access pattern.
- S3 Standard: S3 Standard is intended for frequently used data and provides instant access. It is an excellent choice for services that require high availability, such as web applications and streaming media.
- S3 Infrequent Access: The S3 Infrequent Access tier is intended for data used occasionally and thus offers more affordable pricing. However, it can take longer to access data from this storage class, so it is a good option for storing data such as backups, archives, and object uploads.
- S3 Intelligent-Tiering: S3 Intelligent-Tiering seamlessly transfers data between different S3 storage tiers based on access patterns. Using S3 Intelligent-Tiering can help you save capital on storage fees without compromising performance.
- S3 Glacier: S3 Glacier is an inexpensive archiving and disaster recovery storage service. It offers various retrieval options that balance cost and retrieval speed. Glacier Deep Archive is the least expensive storage class in S3 Glacier, but its retrieval speeds are the slowest. It is suitable for storing rarely accessed data, such as cold backups and historical data.
💡N2W makes it simple to manage your data lifecycling from one S3 or Glacier tier to another to help you save money and meet any retention requirements with ease.
Amazon FSx
Amazon FSx is a managed file storage service that offers a variety of file systems, including Windows File Server, NFS, and Lustre. It is suitable for applications requiring shared file storage across various instances.
- FSx for Windows File Server: A fully managed file server that provides a Windows file system-like experience. It is an appropriate choice for programs that require Windows client compatibility.
- FSx for Lustre: FSx for Lustre is a powerful file system intended for programs with parallel processing. It is an excellent choice for scientific computing and video editing applications.
- FSx for NetApp ONTAP: FSx for NetApp ONTAP is a file system compatible with the iSCSI, SMB, and NFS protocols. It is an effective choice for programs that need Windows, Linux, and macOS client compatibility.
💡N2W supports all versions of Amazon FSx.
Elastic File System (EFS)
Amazon EFS enables multiple EC2 instances to access scalable file storage concurrently. It is ideal for scenarios where multiple instances need access to shared data, such as web servers in a load-balanced environment.
Choosing a Storage Tier
The optimal storage tier depends on your specific needs. Consider the following factors when choosing a storage tier:
- The type of data you are storing: Some storage tiers are better suited for certain data types than others. S3 Standard is a good choice for frequently accessed data, while S3 Glacier is a good choice for rarely accessed data.
- The requirements for your applications’ performance: Some storage tiers provide superior performance. For example, Provisioned IOPS SSD is a good choice for applications that require high IOPS.
- The cost of the storage tier: The cost of different storage tiers varies, so you should choose a storage tier that fits within your budget (more on this below).
Pricing of AWS Storage Tiers
The pricing of AWS storage tiers can often be difficult to gauge; nonetheless, there are some fundamental concepts that can help you better comprehend storage pricing.
S3 Pricing Model
The pricing of S3 is more complex than the pricing of EBS, as it depends on several factors, such as the storage class, the region, the amount of data stored, and the frequency of access.
AWS Storage Costs
The storage costs for S3 are based on the storage class and the region. For example, the storage cost for a 100 GB object in the S3 Standard storage class in the US East (N. Virginia) region is $0.023 per GB per month.
Retrieval Fees
These fees are incurred when you access data from S3 storage classes that charge for retrieval, such as S3 Infrequent Access and S3 Intelligent-Tiering. The retrieval fee is based on the size of the object and the storage class. For example, the retrieval fee for a 100 GB object from the S3 Infrequent Access tier in the US East (N. Virginia) region is $0.00099 per GB.
Data Transfer Costs
Data transfer costs are incurred when you move data to or from an S3 bucket. The cost of transferring data depends on the amount of data and the ultimate destination of the data. For example, the data transfer cost for transmitting 100 GB of data from your S3 bucket in the US East (N. Virginia) region to your computer is $0.09 per GB.
Here is the pricing of AWS storage tiers to give you some idea of the different tiers and their cost differences. These are point-in-time pricing and may change, of course.
| Storage Tier | Storage Class | Region | Storage Cost (GB/month) | Retrieval Fee (GB) | Data Transfer Cost (GB) |
| EBS | General Purpose SSD | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.08 | N/A | $0.09 for First 10 TB / Month |
| EBS | Provisioned IOPS SSD | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.065 per IOPS per month + $0.125 per GB per month | N/A | $0.09 for First 10 TB / Month |
| EBS | Cold HDD | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.015 | N/A | $0.09 for First 10 TB / Month |
| S3 | Standard | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.023 | N/A | $0.09 for First 10 TB / Month |
| S3 | Infrequent Access | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.0125 | $0.00099 | $0.09 for First 10 TB / Month |
| S3 | Intelligent-Tiering | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.023 | $0.00099 | $0.09 for First 10 TB / Month |
| S3 | Glacier | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.004 | N/A | $0.00099 for first 1 GB, then $0.09 per GB |
| S3 | Glacier Deep Archive | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.0009 | N/A | $0.00099 for first 1 GB, then $0.099 per GB |
| FSx | FSx for Windows File Server | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.065 for SSD storage | N/A | $0.09 for First 10 TB / Month |
| FSx | FSx for Lustre | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.145 for SSD storage | N/A | $0.09 for First 10 TB / Month |
| FSx | FSx for NetApp ONTAP | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.0438 for SSD storage | N/A | $0.09 for First 10 TB / Month |
| EFS | EFS | US East (N. Virginia) | $0.043 | N/A | $0.09 for First 10 TB / Month |
You can see nominal pricing differences that line up with associated features and value. Pricing is also adjusted for some regions, in turn affecting cross-region storage. As you scale your storage and overall AWS usage, there may be additional costs associated with transfer, logging, auditing, and other AWS service costs.
Understanding the storage pricing of AWS storage tiers is critical in helping you optimize your storage costs and ultimately save money on your AWS bill.
How to Reduce AWS Storage Costs
Optimizing AWS storage costs involves proactive management and strategic decision-making. You can employ these strategies to achieve cost efficiency:
Keep EC2 Instances and S3 Buckets in the Same Region
By keeping your EC2 instances and S3 buckets in the same region, you reduce data transfer costs and enhance performance. This is particularly useful when applications require frequent data exchange between instances and storage.
S3 Replication to Other Regions
While replicating data to other regions is vital for disaster recovery, it comes with egress and storage costs. Consider the trade-off between redundancy and cost when determining your replication strategy. N2W’ single user dashboard centralizes and simplifies the process of replicating S3 buckets in order to maximize data protection.
Continuously Monitor Which Resources Are Actually Used
AWS offers several tools to help you monitor your AWS resources, such as Amazon CloudWatch and AWS Cost Explorer. By monitoring your resources, you can identify unused resources that you can terminate to save money.
Set up Frequent Alerts and Notifications
You can set up alerts and notifications to be notified when your resources are approaching their limits or when they are not being used. This will prevent wasteful spending on resources that are not used. Note that third party tools like N2W allow you to generate alerts and reports to monitor your resource usage and ensure that you are correctly provisioning your resources.
Delete Irrelevant Files
Regularly review your stored data and delete unnecessary files. This not only frees up storage space, but also reduces related expenses.
Utilize AWS Cost Explorer
AWS Cost Explorer is an effective tool that can assist you in visualizing your AWS costs and identifying cost-saving opportunities.
Delete Dormant EBS Volumes/S3 Buckets
Amazon EBS volumes and S3 buckets that are not in use can continue to incur charges, so you should delete dormant volumes and S3 buckets to save money. This ought to be included in your data protection and recovery plan so that you are storing dormant volumes and snapshots in an optimized way.
Optimizing data protection storage also contributes to your general AWS storage costs. This is where a tool like N2W is critical because you can determine how many disaster recovery copies you want to store (which can be different from the number of backup snapshots) —meaning you don’t have to pay 2x the storage cost to have disaster recovery enabled.
Create Automated EBS Deletion Policies
When an EC2 instance is stopped, the EBS volume attached to the instance is also stopped. You can still incur charges for the Amazon EBS volume even if the instance is stopped. EBS does not charge for detached volumes, but storage costs are still incurred.
💡N2W allows you to automatically delete EBS snapshots when archiving to S3/Glacier with our ZeroEBS feature.
Keep Default EBS Deletion Policies
Make sure that you do not modify the termination behavior of your AWS EBS and EC2. Using the default policy to delete persistent EBS volumes along with the termination of the EC2 instance helps reduce orphaned volumes. Again, this is something that needs to be accounted for in your data retention policies for snapshots and the overall data protection process.

- Use Lifecycle Policies to Save Money: Set up lifecycle policies to move old backups to cheaper storage options like Amazon S3 Glacier. This can help you save a lot of money on storage costs.
- Back Up to Different Regions and Accounts: Make your disaster recovery plan stronger by copying backups to different AWS regions or accounts. This protects your data from region-specific problems and security issues.
- Automate Your Backup to Reduce RTO: Use AWS Backup to set up frequent backup intervals. Automating backups every hour or even every few minutes ensures you can recover data quickly, minimizing downtime.
- Tag Your Resources for Easy Management: Tags help you quickly identify and group related backups, making it easier to manage them and to monitor costs. This can also simplify reporting and compliance checks.
- Test Your Disaster Recovery Plan Regularly: Automate DR drills to check your backup and recovery processes. Make sure your backups work and that you can restore data quickly to find and fix any potential problems.
Archival From Amazon EBS to Cheaper/Colder Storage
If you have data that you do not need to access frequently, you can archive it to a cheaper/colder storage tier, such as S3 Infrequent Access or Glacier. This can help reduce your storage costs. Here’s an overview of the different S3 storage classes that AWS offers:
- S3 Standard: S3 Standard is the default Amazon S3 storage tier for frequently accessed data. It offers the lowest latency and highest availability.
- S3 Infrequent Access: The S3 Infrequent Access tier is intended for data that doesn’t need to be available immediately. It offers less expensive storage costs than S3 Standard.
- S3 Intelligent-Tiering: S3 Intelligent-Tiering automatically moves data between different S3 storage tiers based on access patterns. This can reduce your storage costs without affecting performance.
- Glacier Instant Retrieval: Glacier Instant Retrieval is a tier of Glacier that offers faster retrieval times than the standard Glacier tier. This is a great option for data that needs to be quickly accessible but isn’t frequently used.
- Glacier Deep Archive: This is the storage tier within S3 Glacier that provides the lowest cost. It is the best option for data that seldom needs to be accessed.
💡With N2W you can automate data archival for smooth and continuous AWS cost optimization.
Conclusion
AWS storage costs can be complex, but by understanding the factors that influence storage pricing, the different storage tiers available, and the strategies for optimizing costs, you can make informed decisions about your storage needs.
Here are some key considerations to be mindful of when optimizing your AWS storage costs:
- The type of data you store: Taking advantage of multiple storage tiers is ideal for storing different types of data. For example, S3 Standard is a good choice for frequently accessed data, while S3 Glacier is a good choice for rarely accessed data.
- The performance requirements of your workload: Some storage tiers offer better performance than others. For instance, Provisioned IOPS SSD is a good choice for applications that require high IOPS.
- The cost of the storage tier: The cost of different storage tiers varies greatly, so it’s important that you choose a storage tier that fits within your budget.
Once you understand these factors, you can start to optimize your storage costs by choosing the storage class that is most appropriate for how you need to access your data. Keep in mind that AWS provides several cost management tools like AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets that can be used to monitor and control your storage costs. But if reducing costs is really important for your team, then a tool like N2W is a great option for optimization.
By adopting the aforementioned tips, you can optimize your storage costs through methods such as deleting unused data, archiving data to cheaper storage tiers, and taking advantage of reserved instances. We hope you take advantage of all these strategies so that you can optimize your storage costs and ultimately cut down on your AWS bill!
N2W takes the guesswork—and the heavy lifting—out of storage optimization and disaster recovery:
- Automated Tiering & Archival: Seamlessly migrate cold snapshots from EBS to cheaper S3, Glacier, or any cloud you choose—so you never overpay for idle data.
- ZeroEBS Snap Cleanup: Automatically delete obsolete EBS snapshots once they’re safely archived, eliminating orphaned volumes and phantom charges.
- Cross-Cloud Flexibility: Store backups across AWS, Azure, and Wasabi from a single pane of glass—so you can balance cost, compliance, and recovery speed without juggling multiple tools.
- Policy-Driven Lifecycle & Retention: Define RPOs/RTOs and let N2W enforce them—moving, locking, or deleting backups exactly when you need.
- Real-Time Visibility & Alerts: Get instant insights into your storage spend, backup success rates, and lifecycle events—so you catch misconfigurations or cost spikes before they bite.
With N2W, you’re not just optimizing AWS storage—you’re armed with a fully automated, cloud-agnostic data-protection engine designed to slash costs, simplify operations, and keep your business running.
